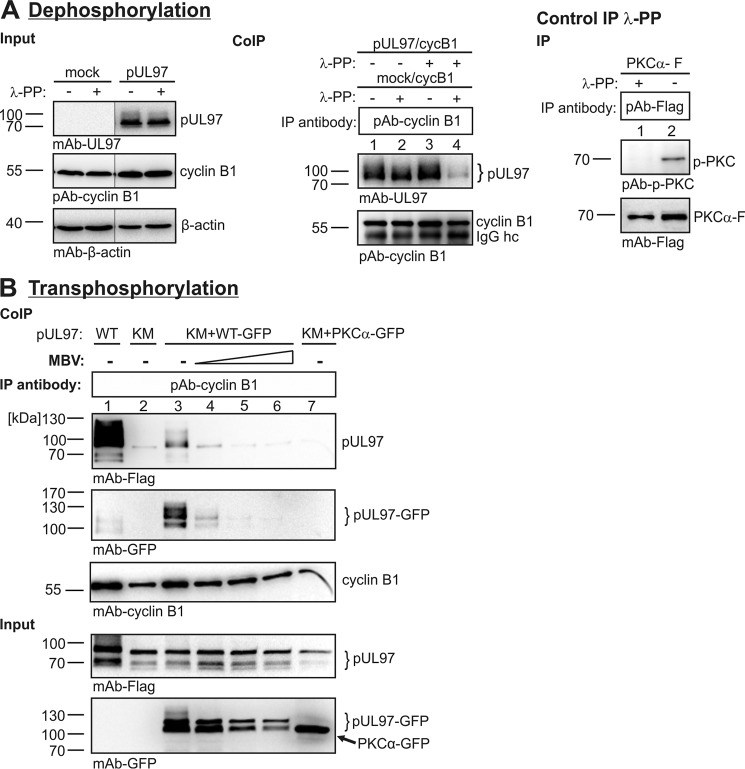
Figure 4.
Interaction between pUL97 and cyclin B1 depends on the state of phosphorylation, as shown by dephosphorylation (A) and transphosphorylation (B) analyses. A, dephosphorylation of protein lysates from transfected 293T cells (3 days post-transfection) expressing pUL97 or vector control (mock) was performed using λ-phosphatase (λ-PP; 30 min, 30 °C). Immunoprecipitation (IP) of cyclin B1 was performed using combinations of input samples, either untreated or treated with λ-PP. A positive control reaction confirmed the λ-PP activity using a phospho-specific antibody against PKCα. B, transfection of 293T cells expressing the WT version of pUL97–FLAG (WT) or the inactive mutant K355M (KM), optionally cotransfected with a larger-size version pUL97–GFP (WT–GFP). PKCα-GFP was used as a reference kinase lacking pUL97 activity. The transphosphorylation samples were harvested at 3 days post-transfection and used for cyclin B1–specific CoIP. MBV, pUL97 inhibitor maribavir applied at the concentrations 0.2, 1, and 10 μm (lanes 4–6). Note that Western blotting splicing was performed to integrate the relevant lanes as indicated by vertical marking lines.