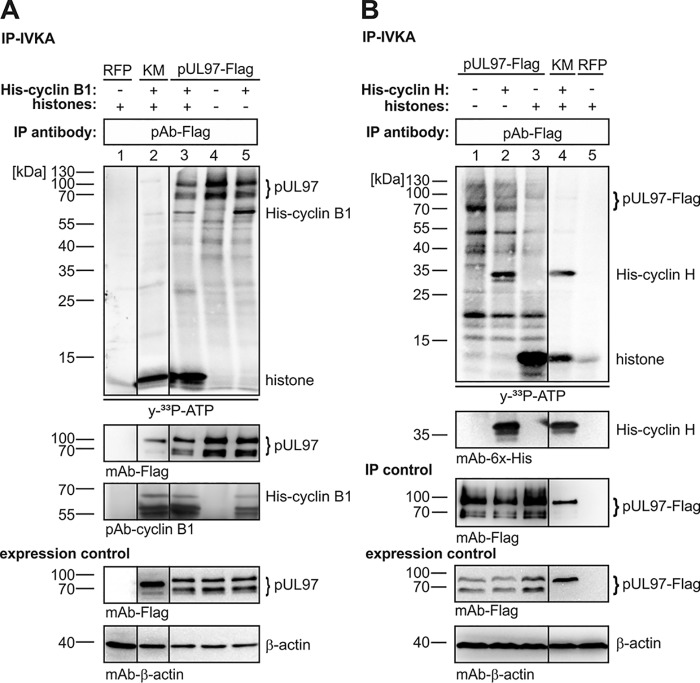
Figure 5.
pUL97-specific IVKA determining the putative modulatory effect of cyclin B1 (A) or H (B) association on pUL97 activity. Transiently expressed pUL97–FLAG or pUL97(K355M)–FLAG (KM) were harvested 3 days post-transfection in a cyclin-avoiding fashion by applying high-stringency IP (500 mm NaCl buffer) to remove associated cyclins (for cyclin B1 monitored on WB). The two versions of pUL97 were subjected to IVKA reactions under standard conditions. Each reaction was supplemented by the addition of either human cyclin B1 (A, 2 μg), human cyclin H (B, 5 μg), or human histones (20 μg) as indicated. Upper panels, IVKA (autoradiogram) and detection of His–cyclin B1/His–cyclin H on the IVKA membrane (WB restaining); middle panel, detection of comparable pUL97 levels (precipitation control); lower panels, total input levels contained in cell lysates (expression control). Red fluorescent protein (RFP; A, lane 1; B, lane 5) was used as negative control. Note that Western blotting splicing was performed to integrate the relevant lanes as indicated by vertical marking lines.