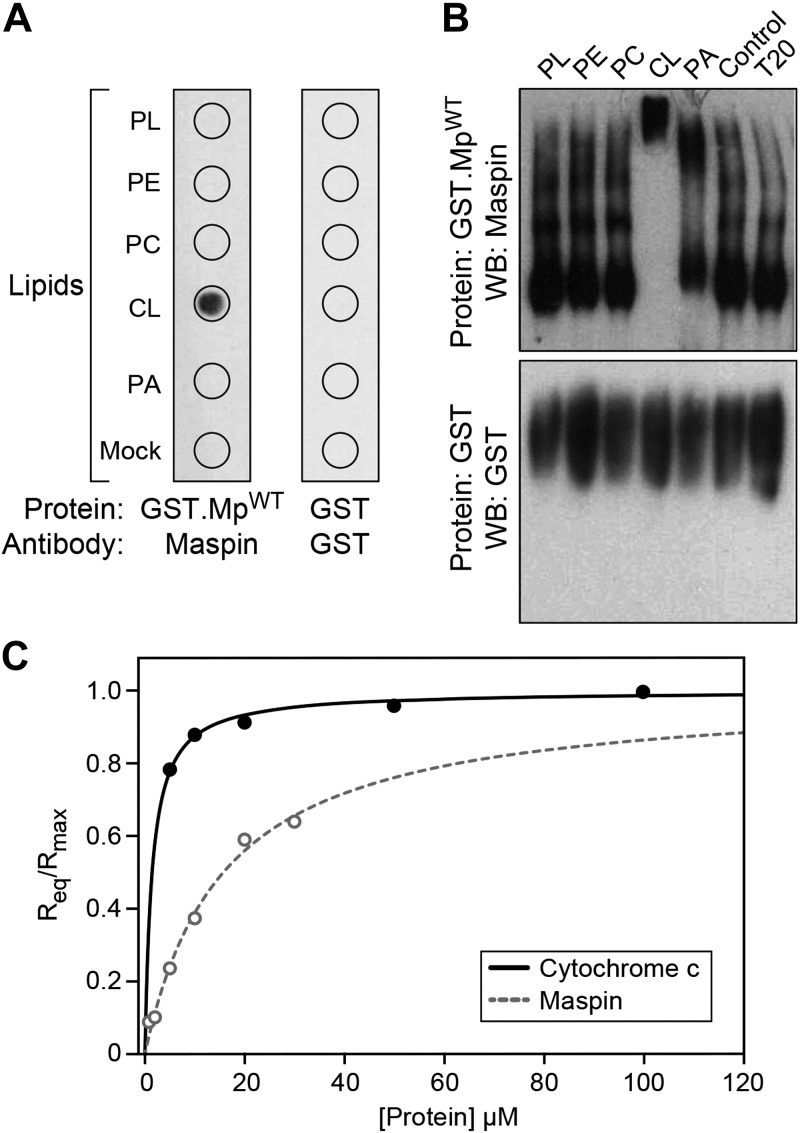
Figure 1.
Maspin binds to CL. A) A protein-lipid overlay assay demonstrating the interaction between maspin and various lipids [phospholipids (PL), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), PC, CL, phosphatidic acid (PA), BSA (Mock)]. Wild-type maspin (GST.MpWT) binds specifically to CL and not to the other lipids tested. GST protein (as control) did not bind to the lipids. B) Binding of maspin to CL was determined by retardation of protein mobility in a PAGE–Western blot (WB). T20, Tween 20. Incubation of GST.MpWT with CL reduced the mobility of the protein in contrast to the other lipids. GST was used as a control. C) Dependence of the equilibrium and maximal wavelength shift (Req and Rmax) on protein concentration. Liposomes (50:50 PC:CL by molar concentration) were immobilized on the surface of APS biosensor tips. The interaction between vesicles, cytochrome c (solid line), and maspin (dotted line) was monitored until equilibrium was reached in 25 mM HEPES pH 7.4. Fit to Eq. 1 yielded the apparent association constants (Ka) of 6.9 × 105 M−1 and 6.3 × 104 M−1 for cytochrome c and maspin, respectively. All data points represent means ± sd (n = 3). Representative figures are shown of experiments completed a minimum of 6 times.