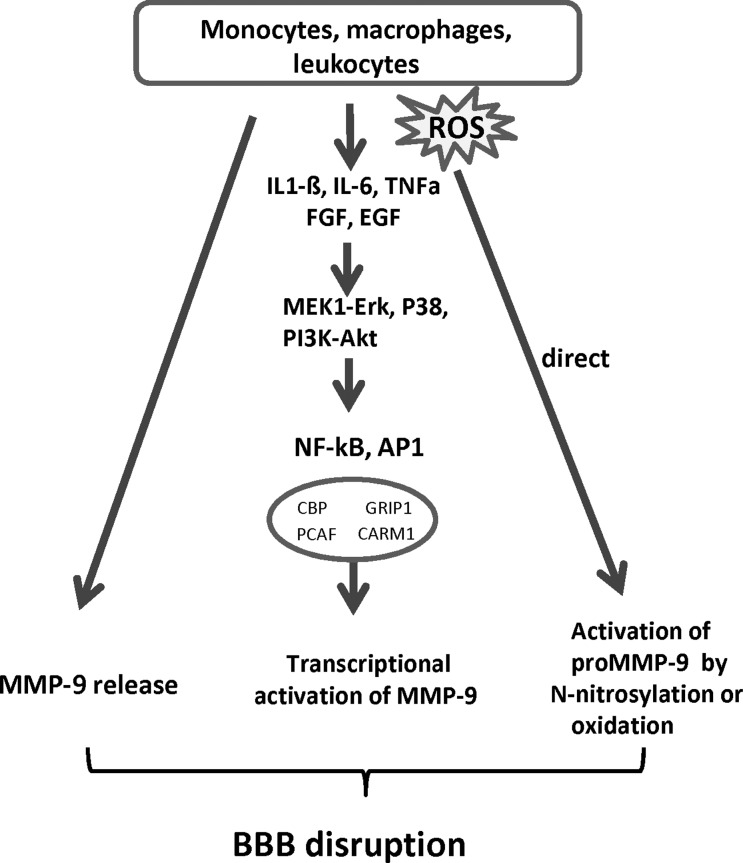
FIG. 6.
Inflammatory cells contribute to the elevation of MMP-9 levels in neural tissue and cEC constituting the BBB. Monocytes, macrophages and leukocytes play a critical role in many pathological conditions, including oxidative stress. They are a major source of MMP-9 and ROS attacking the BBB. In addition, they release inflammatory cytokines and growth factors, such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, TNFα, FGF, EGF, which can stimulate the production and secretion of MMP-9 in all cells constituting the BBB. The signaling pathways involved include activation of MEK1-Erk, MAPK P38, and PI3K-Akt. Transcription of MMP-9 is regulated through activating AP-1 and NF-kB, which subsequently bind to cis elements on the MMP-9 promoter. AP-1 and NF-kB act in concert with various chromatin remodeling complexes and co-activators to induce MMP-9 expression. These include CBP/P300, PCAF, CARM1, and GRIP-1/SRC-2. Protease-independent activation of MMPs occurs by S-nitrosylation or oxidation to unmask the catalytic domain without pro-domain cleavage (citations are given in the text). AP-1, activator protein-1; CARM1, coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1; CBP, CREB-binding protein; CREB, cAMP-response-element binding protein; EGF, epidermal growth factor; ERK, extracellular signal activated protein kinase; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; GRIP-1, glucocorticoid receptor interacting protein-1; MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase; MEK1-ERK, mitogen activated ERK activating kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; PCAF, p300/CBP associated factor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; SRC-2, steroid receptor coactivator-2; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha.