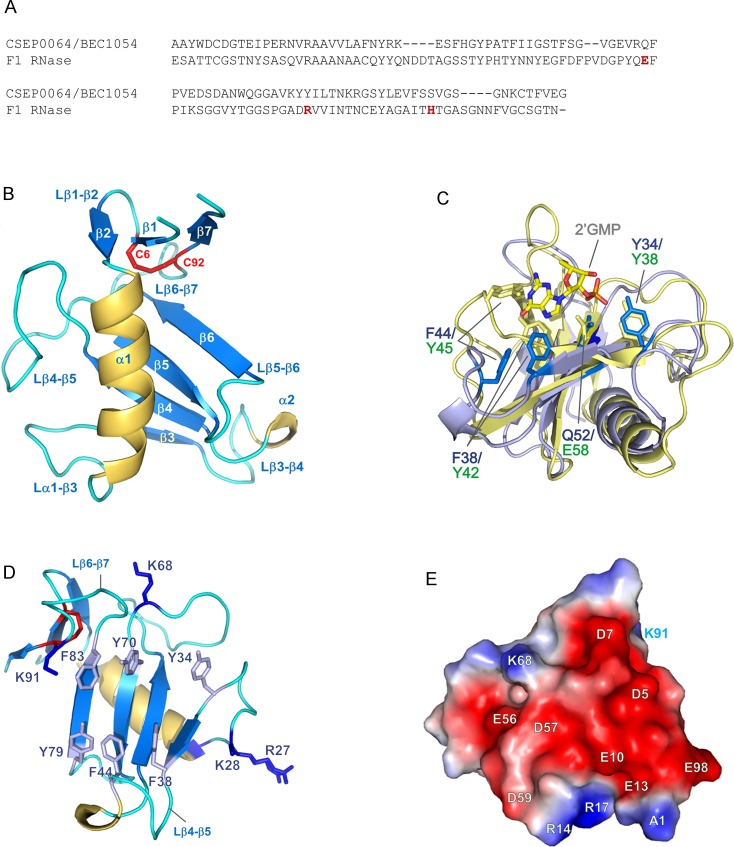
Fig 3. Structural details of CSEP0064/BEC1054.
(A) Structure-based sequence alignment of CSEP0064/BEC1054 and the F1 RNase from F. moniliforme. Residues forming the catalytic triad in the F1 RNase are marked in red. (B) CSEP0064/BEC1054 (PDB ID 6FMB) exhibits a canonical T1 RNase type fold, including a disulphide bridge between C6 and C92 linking the N- and C- termini of the protein (shown in red). (C) Structural overlay of CSEP0064/BEC1054 (backbone in light blue) with F1 RNase from F. moniliforme (backbone in yellow, PDB ID 1FUT). These structures share an RMSD of 2.3 Å over 64 Cα atoms. Residues of the F1 RNase that bind 2’GMP are highlighted in yellow and functionally equivalent residues in non-catalytic CSEP0064/BEC1054 in marine blue. For clarity, the side chains of Y70 (in CSEP0064/BEC1054) and R77 (in F1 RNase) are not shown. (D) Exposed aromatic side chains in the large β-sheet and the β1-β3, β3-β4 loops cluster on the concave face of the CSEP0064/BEC1054 protein. Side chains of positively charged side chains at the edges of the concave face are also shown. (E) Electrostatic surface potential calculated using APBS [30], shows a patch (shown in red) of negatively charged residues on the surface of CSEP0064/BEC1054.