Figure 5. Extracellular PDI and GPIbα contribute to tissue damage in I/R-induced stroke and cell-cell aggregation and vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease.
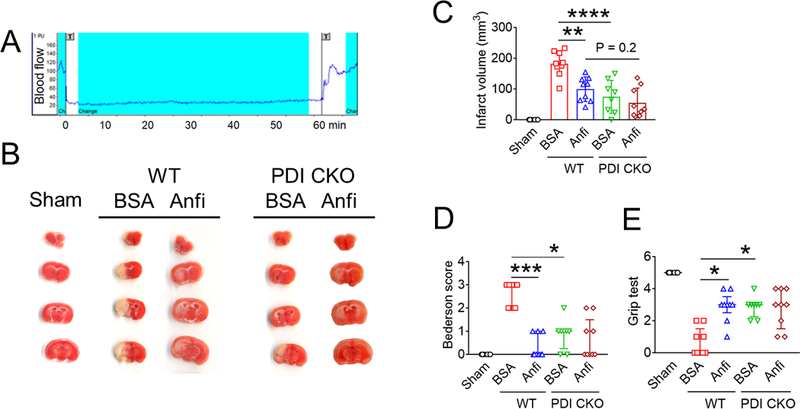
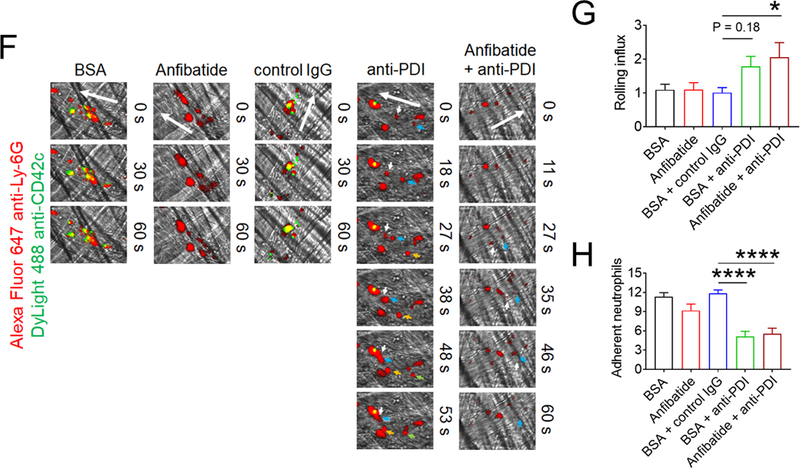
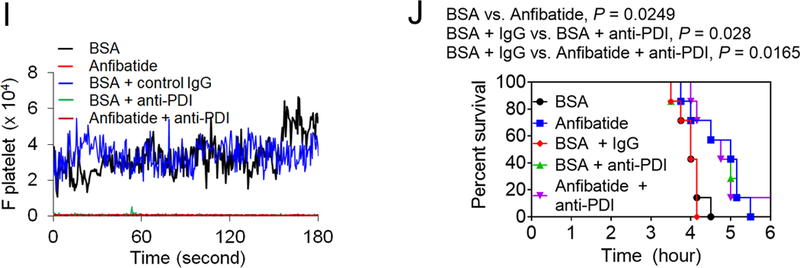
(A-E) Stroke was induced in WT and platelet-specific PDI CKO mice by transient MCAO and reperfusion as described in Methods. BSA or Anfibatide (5 ng/g BW) was intravenously infused into mice right after 1-hour MCAO. (A) MCAO and reperfusion were confirmed by a laser Doppler flowmeter. (B) Staining of coronal brain sections with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride. (C) The infarct volume was measured. (D-E) The Bederson score and grip test were used to analyze neurologic deficits in the surviving animals 24 hours after MCAO. Data represent the mean ± SD except for the Bederson score and the grip test score, which are shown as scatter plots including median with interquartile range (n = 8–9 mice per group). (F-J) SCD mice were treated with intraperitoneal injection of TNF-α. BSA or Anfibatide (25 ng/g BW), control IgG or blocking anti-PDI antibodies (1.5 μg/g BW), or both inhibitors were infused into mice 3 hours after TNF-α injection. Platelets and neutrophils were visualized as described in Figure 4. (F) Representative images. Large and small arrows show the direction of blood flow and rolling neutrophils, respectively. (G-H) The numbers of rolling and adherent neutrophils were counted. (I) The integrated median fluorescence intensities of anti-CD42c antibodies (F platelets) were normalized to the number of adherent neutrophils and plotted as a function of time. (J) Survival curves. Survival times were significantly prolonged in the groups treated with an anti-PDI antibody, Anfibatide, or both inhibitors, compared to each control. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 7–8 mice per group), *:P<0.05, **:P<0.01, ***:P<0.001, or ****:P<0.0001 after ANOVA and Tukey’s test (C, G and H), Kruskal-Wallis test with post hoc Dunn correction (D and E), or Mantel-Cox log-rank test (J).
