Figure 7.
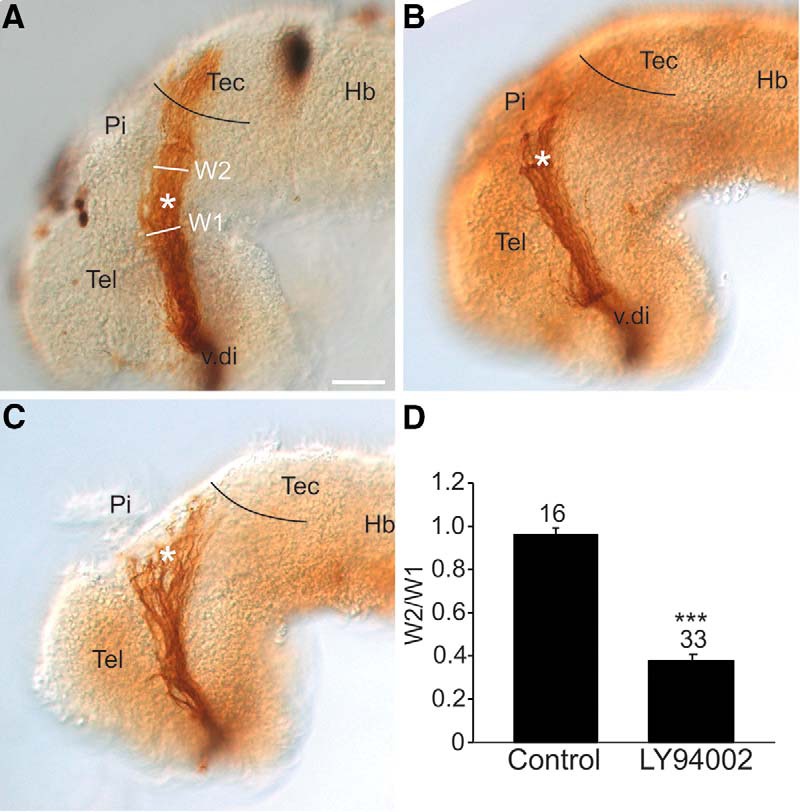
PI3K signaling regulates the behavior of RGC axons at the mid-diencephalic turn. Lateral views of stage 40 wholemount brains with HRP-labeled optic tracts that were exposed at stage 33/34 either to (A) control DMSO solution (n = 16 brains, N = 3) or (B, C) 20 µM LY294002 (n = 33 brains, N = 3). Black line represents the approximate anterior border of the optic tectum, and the asterisk the location of the mid-diencephalic turn guidance choice point. D, The RGC axon stall phenotype was quantified by representing the width of the optic tract post-mid-diencephalic turn (W2) as a ratio (W2/W1) to the width of the optic tract (W1) at the mid-diencephalic turn. On each bar is the number of individual brains pooled from 3 independent experiments. Bars represent the mean ± SEM; ***p < 0.001 using the unpaired Student’s t test. Scale bar, 50 µm. Hb, hindbrain; Pi, pineal gland; Tec, tectum; Tel, telencephalon; v.di, ventral diencephalon.
