Figure 1.
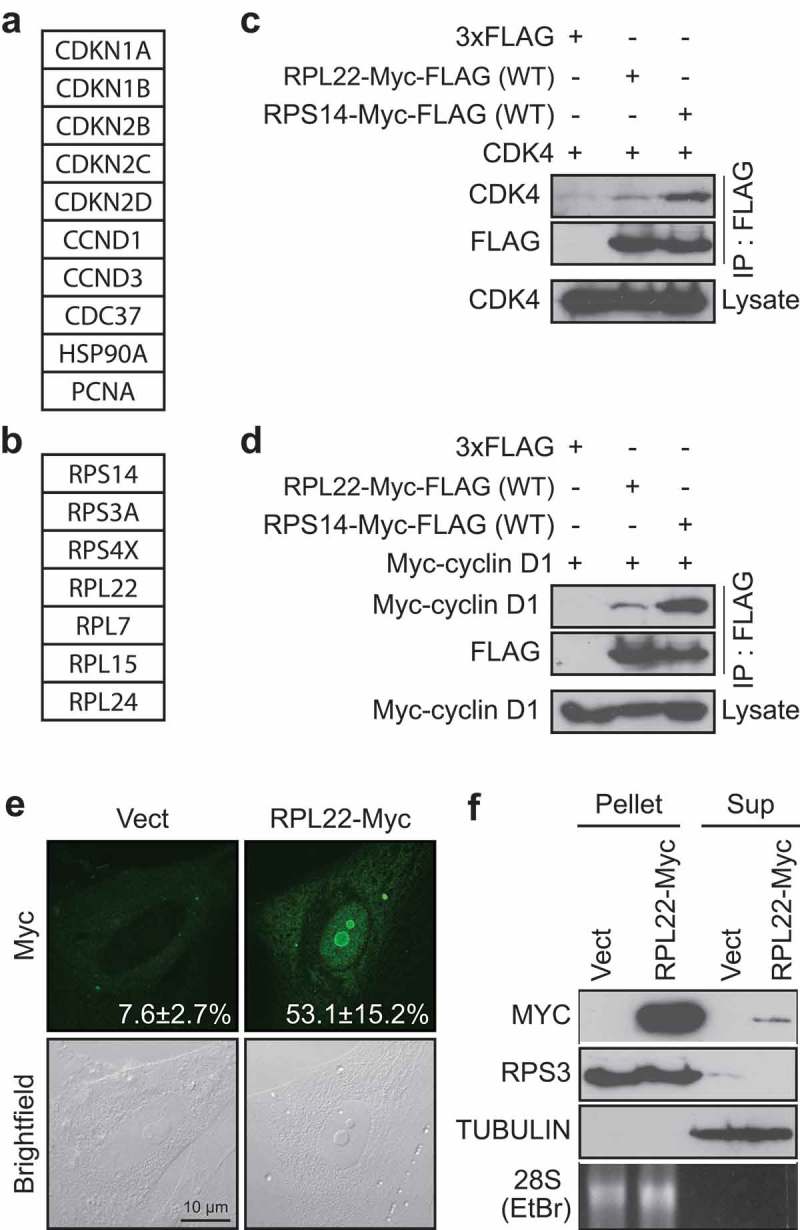
RPL22/eL22 can interact with CDK4 and/or cyclin D1 (a, b) List of selected proteins found to immunoprecipitate with a FLAG-tagged version of CDK4(K35M) from RSL1D1 knockdown-induced senescent cells classified as known interactors of CDK4 (a) and ribosomal proteins interactors (b). (c) HEK-293T cells were transfected with vectors expressing CDK4 and 3xFLAG control, Myc-FLAG tagged RPL22 wild type (RPL22-Myc-FLAG(WT)) or Myc-FLAG tagged RPS14 wild type (RPS14-Myc-FLAG(WT)) and immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody. Lysates and immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. (d) HEK-293T cells were transfected with vectors expressing Myc-cyclin D1 and 3xFLAG control, RPL22-Myc-FLAG(WT) or RPS14-Myc-FLAG(WT) and immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLAG antibody. Lysates and immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for the indicated proteins. (e) Indirect immunofluorescence (IF) with a specific anti-Myc tag antibody showing RPL22-Myc in IMR90 cells expressing an empty control vector (Vect) or RPL22-Myc at day 12 post-infection (representative images). Data were quantified from 3-independent cell counts up to a total of at least 100 cells in triplicate and are presented as the mean percentage of positive cells for nucleolar localization of RPL22-Myc ± SD. Brightfield images are shown alongside. Scale bar, 10 µm. (f) Immunoblots for the indicated proteins and ethidium bromide detection of 28S rRNA in ribosome purification by sedimentation (Pellet) or its supernatant (Sup) obtained from extracts of IMR90 cells expressing RPL22-Myc or an empty control vector (Vect) at day 7 post-infection. Blots in C, D and F are representative of 3 independent experiments with similar results.
