Figure 2.
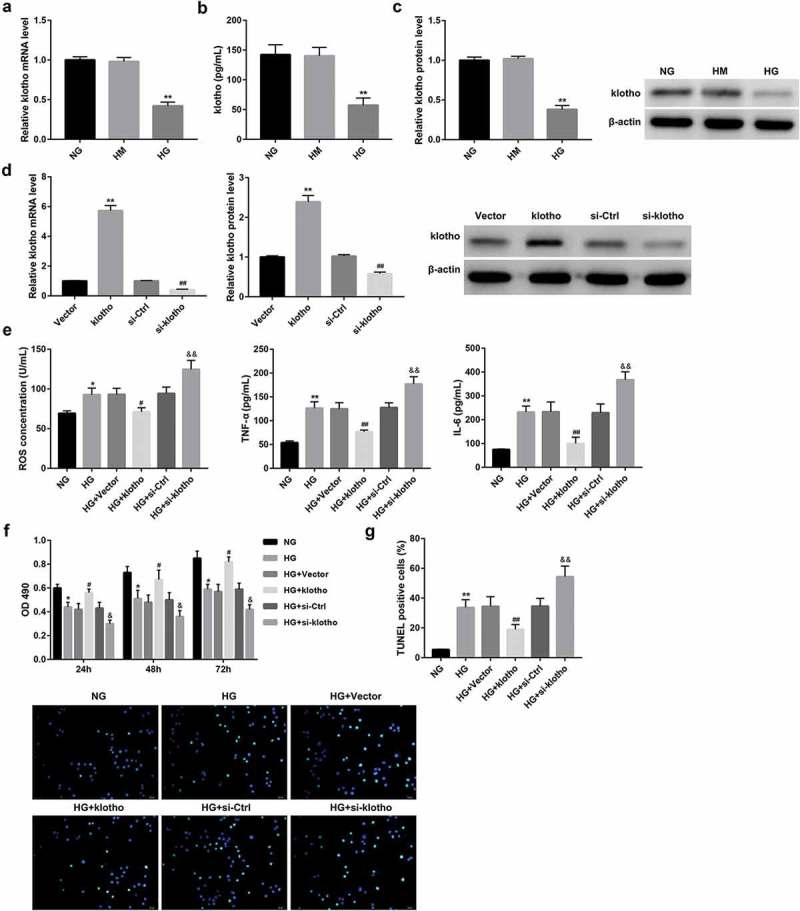
Klotho overexpression significantly abolished the HG-induced HRGECs injury.
The mRNA (a) and protein (c) expression of klotho in HRGECs, as well as secretion of klotho (b) from HRGECs which were cultured with NG (5.6 mmol/L D-glucose), HM (5.6 mmol/L D-glucose plus 14.4 mmol/L mannitol), and HG (20 mmol/L D-glucose) for 24 h, were examined by RT-qPCR, western blot, and ELISA, respectively. **p < 0.01 vs. the HM group. In another experiment, HRGECs were transfected with pcDNA3.1-klotho, empty pcDNA3.1 vector, si-klotho, or si-Ctrl followed by HG stimulation for 24 h. (d) The overexpression and knockdown efficiency of klotho in HRGECs 48 h post-transfection was confirmed by RT-qPCR and western blot. **p < 0.01 vs. the vector group, ##p < 0.01 vs. the si-Ctrl group. The effect of klotho expression on levels of ROS, TNF-α, and IL-6 (e) in HRGECs, plus HRGECs proliferation (f) and apoptosis (g) was examined using ELISA, MTT, and TUNEL staining method, respectively. Data are presented as the means ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. the NG group, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs. the HG+vector group, &p < 0.05, &&p < 0.01 vs. the HG+si-Ctrl group.
