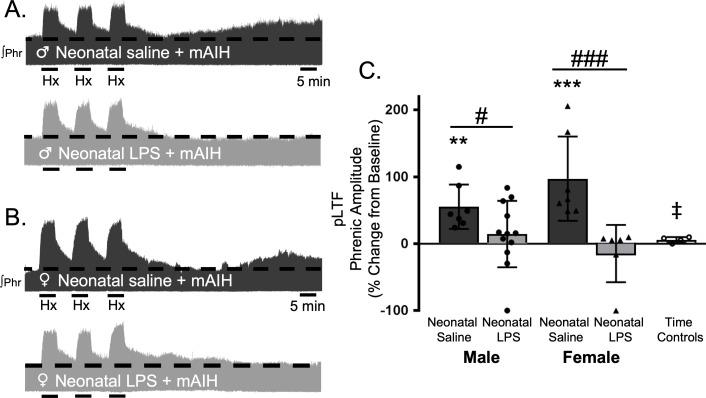
Figure 2. Neonatal systemic inflammation undermines adult, Q-pathway-evoked pLTF in male and female rats.
Representative integrated phrenic neurograms from male (A) and female rats (B) after neonatal (P4) saline (top traces, black) or LPS (1 mg/kg, i.p.; bottom traces, grey). Q-pathway-evoked pLTF is evident in adults after neonatal saline as the progressive increase in phrenic nerve amplitude from baseline (dashed line) over 60 min following moderate acute intermittent hypoxia (mAIH, 3 × 5 min episodes, PaO235–45 mmHg). Group data (C) demonstrate Q-pathway-evoked pLTF 60 min after mAIH is abolished in adults by neonatal LPS in both males (circles) and females (triangles) and no change in phrenic amplitude in time controls (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 from baseline, # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001 between groups, ‡ p < 0.05 from adult males and females after neonatal saline).