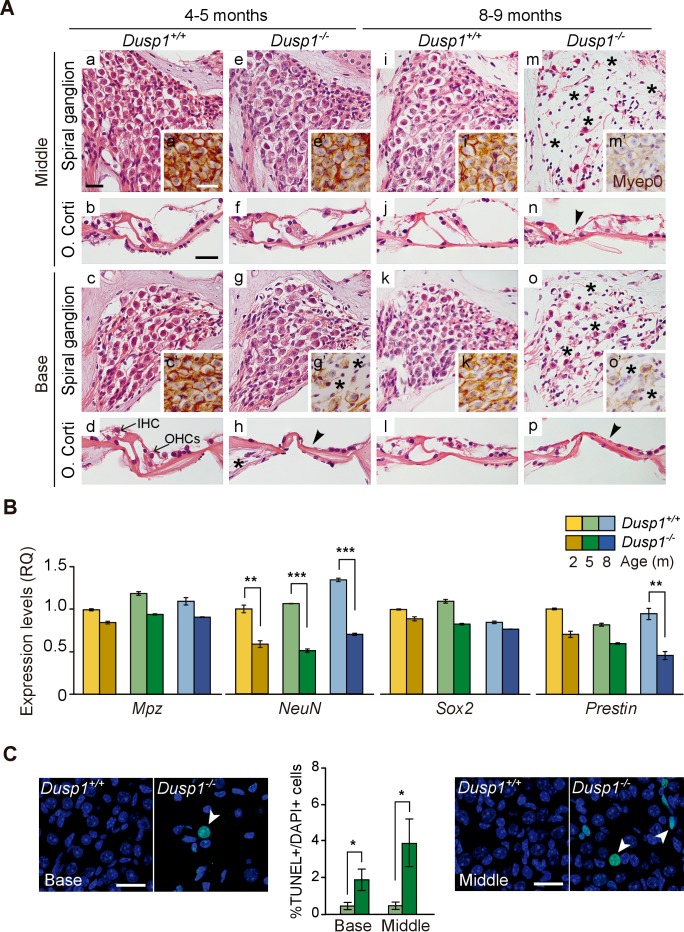
Figure 3. Comparative cochlear cytoarchitecture of Dusp1+/+ and Dusp1–/– mice.
(A) Representative microphotographs of hematoxylin-eosin-stained paraffin cochlear mid-modiolar sections of Dusp1+/+ and Dusp1–/– mice, showing the spiral ganglion and the organ of Corti from the middle and basal turns of the cochlea at 4–5 (n = 5 per genotype) and 8–9 months of age (n = 5 per genotype). Insets present representative microphotographs of myelin protein p0 immunohistochemistry from the middle and basal turns of the cochlea at 4–5 (n = 3 per genotype) and 8–9 months of age (n = 3 per genotype). Asterisks and arrowheads indicate the absence of neural and hair cells, respectively. Scale bars: 25 µm. IHC, inner hair cell; OHC, outer hair cell. (B) Cochlear gene expression of Mpz, NeuN, Sox2 and Prestin in Dusp1+/+ (lighter color bars) and Dusp1–/– mice (darker color bars) at 2, 4–5 and 8–9 months of age. Expression levels were measured by RT-qPCR and calculated as 2–ΔΔCt (RQ), using Rplp0 as reference the gene and normalized to the 2-month-old wildtype mice group. Values are presented as mean ± SEM of triplicates from pool samples of three mice per condition. Statistically significant differences were analyzed by Student’s t-tests comparing genotypes (**p<0.01 and ***p<0.001). (C) TUNEL apoptosis detection. Representative confocal maximal projection microphotographs show the spiral ganglion of the middle and basal turns of 4–5 month-old Dusp1+/+ (light green bars, n = 4) and Dusp1–/– (dark light bars, n = 3) mice. Arrowheads indicate positive TUNEL cells. Quantification of positive TUNEL cells is shown as the percentage of total DAPI-positive cells in a region of interest (ROI) in the spiral ganglion. Values are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistically significant differences were analyzed by Student’s t-tests comparing genotypes (*p<0.05). Scale bar: 25 µm.