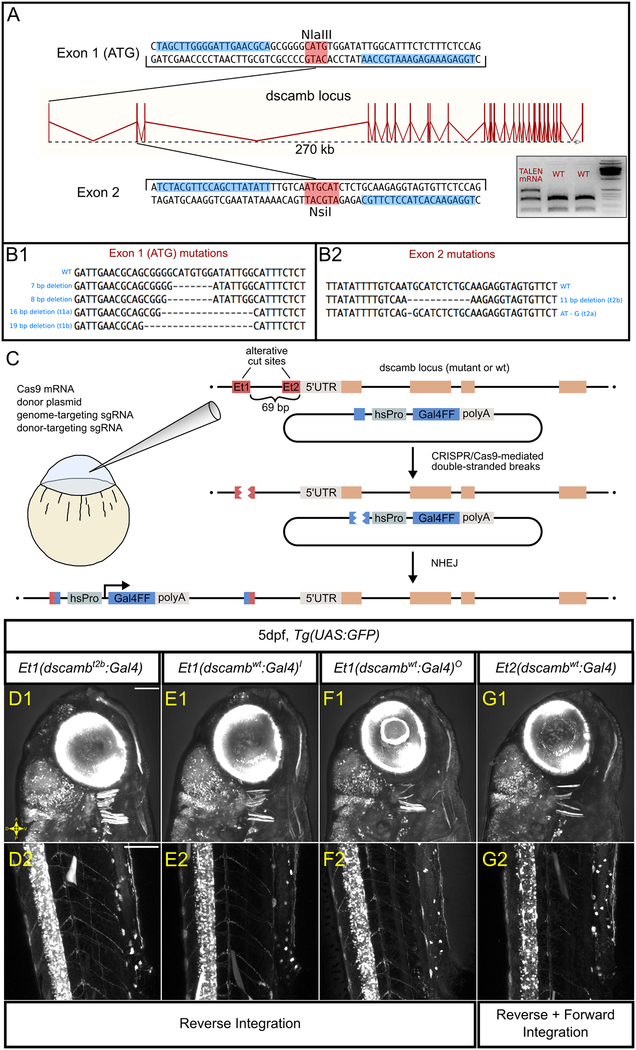
Figure 1 – Using targeted mutagenesis to generate dscamb loss-of-function mutants and enhancer trap reporters.
A) The dscamb locus, including TALEN target sites in exon 1 (top) and exon 2 (bottom). Blue boxes indicate TALEN binding sites. Red boxes indicate restriction enzyme sites used for RFLP genotyping. Inset is an example of RFLP genotyping for mutations at exon 2 using genomic DNA from pooled embryos injected with TALEN-encoding mRNA or uninjected. The upper, uncut band in TALEN-injected embryos indicates mutation of the NsiI site. Gene diagram adapted from Ensembl.
B) TALEN-generated germline mutations at exon 1 (B1) and exon 2 (B2) sites.
C) CRISPR/Cas9 strategy for enhancer trap insertion.
D-G) Representative confocal images of independent enhancer trap lines, showing reporter expression in the head (D1, E1, F1, G1) and trunk (D2, E2, F2, G2). Scale bars = 100 um.