Fig. 4.
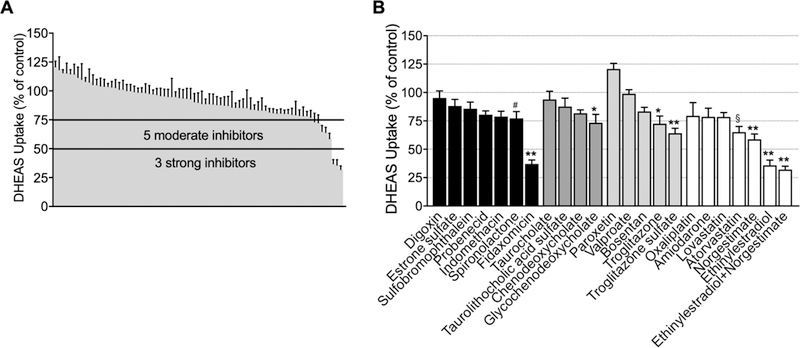
The inhibitory effect of test compounds or fixed-dose combinations on OSTα/β-mediated dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) uptake in OSTα/β-overexpressing (OSTab) cells. A) Compounds or fixed-dose combinations inhibiting DHEAS transport by >50% were denoted as strong inhibitors (n = 3), and those that inhibited between 25% and 50% of the DHEAS transport were designated as moderate inhibitors (n = 5). B) The compounds, illustrated in groups, were previously reported OSTα/β substrates or inhibitors (black), bile acids elevated in cholestasis (dark grey), classical hepatotoxic compounds (light grey), and compounds associated with cholestatic DILI from the Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN) database (only compounds inhibiting DHEAS transport by >20% (white) are shown). The inhibition was studied using Method 1. OSTab and Mock cells were preincubated with putative inhibitor at a concentration of 100 μM for 10 min; the probe substrate, [³H]-DHEAS, was added in extracellular fluid (300 nCi/ml; 4 µM final concentration; pH 7.4) and 30-s uptake was measured at 37°C; inhibition was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Each value represents the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. **p< 0.0001; *p<0.0005; §p<0.05; #p<0.01 significantly different than substrate uptake in control group.
