Figure 3:
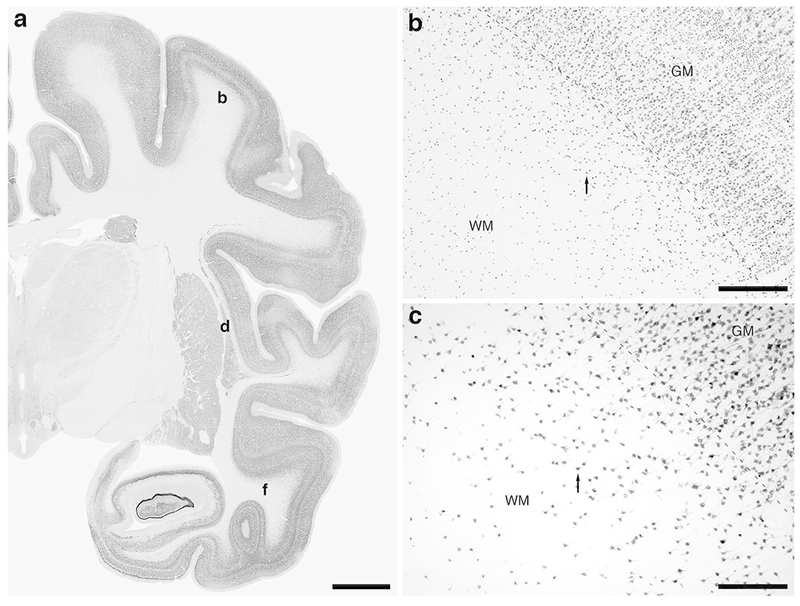
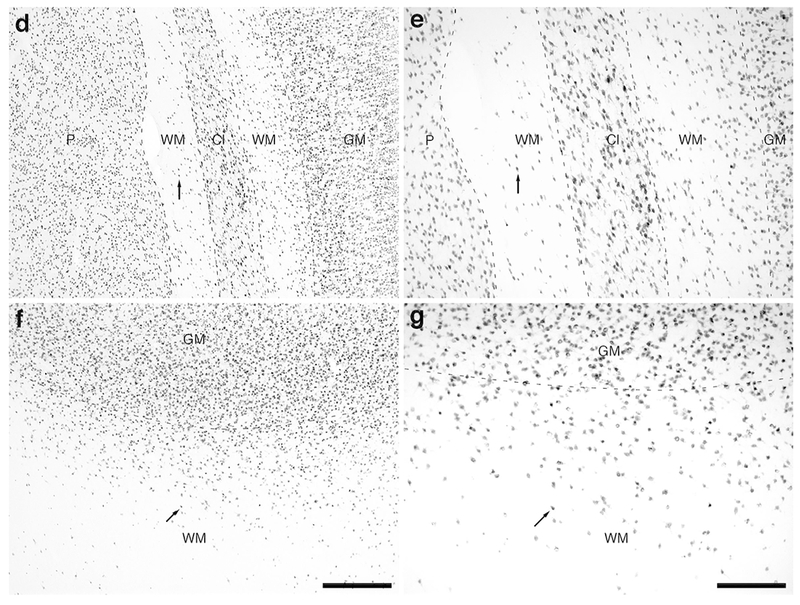
Photomicrographs of NeuN immunostaining in a coronal section through the rostral portion of the parietal lobe, the claustrum/insular cortex and the temporal lobe of the lar gibbon, showing the distribution of WMICs. All conventions as in Fig. 1. (a) Low magnification image of the entire section stained with NeuN, showing the high density of cells within the cerebral cortex and the presence of numerous cells deep to the cortex. (b) Moderately magnified image of the somatosensory cortex (from the region indicated by the b in image a), showing the numerous WMICs deep to the cerebral cortex (grey matter, GM). (c) High magnification image of the cortical/white matter boundary (marked by a dashed line) of the somatosensory cortex, showing the WMICs. (d) Moderately magnified image showing the putamen nucleus (P), claustrum (Cl) and insular cortex (GM), from the region indicated by the d in image a, showing WMICs within the deep WM. (e) High magnification image of the claustrum and surrounding white matter, showing the WMICs in the deep WM. (f) Moderately magnified image of the temporal cortex (from the region indicated by the f in image a), showing WMICs deep to the cerebral cortex within the WM. The approximate boundary of the deep border of cortical layer VI and the WM is marked by a dashed line. (g) High magnification image of the cortical/white matter boundary (marked by a dashed line) of the base of the temporal cortex, showing the WMICs deep to the temporal cortex within the WM. Scale bar in a = 5 mm and applies to a only. Scale bars in b and f = 500 μm and applies to b, d and f. Scale bars in c and g = 250 μm and applies to c, e and g. In all images dorsal is to the top of the image and medial to the left.
