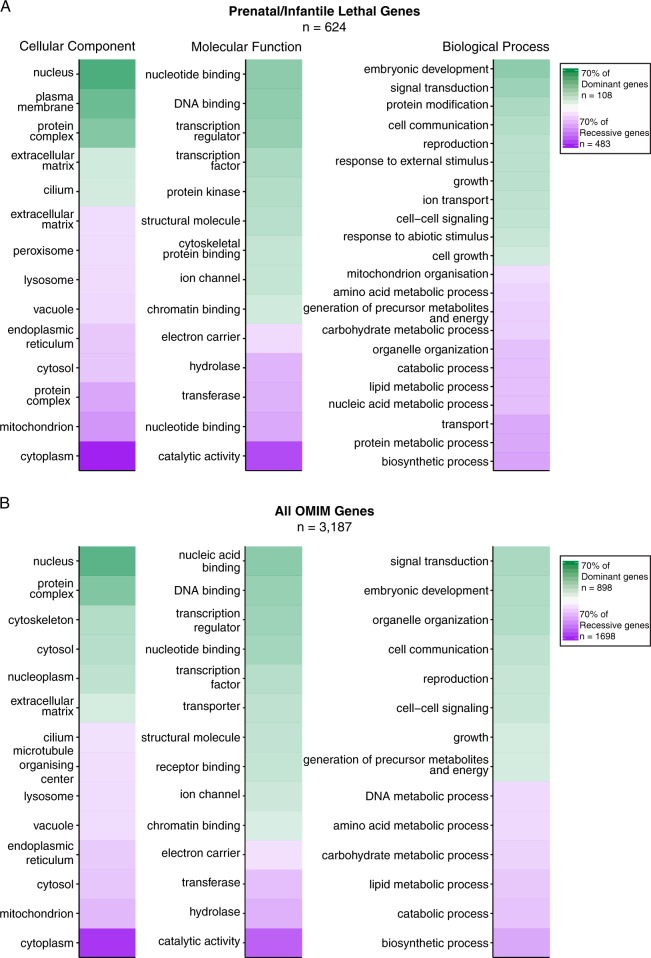
Fig. 4.
Ontology analysis of 624 known prenatal-lethal genes, compared with all 3187 OMIM genes. a Comparative analysis of gene ontology between dominant (AD or X-linked dominant) and recessive (AR or X-linked recessive) prenatal-lethal genes. Gene ontology terms for each gene were compiled, then GO terms comparatively enriched in either dominant or recessive gene families were determined (subcellular localisation, molecular function and biological processes). Comparative metrics were exported from cytoscape with a p-value cutoff of 0.025 with data visualisation performed in R. Green: GO terms significantly comparatively enriched among Dominant lethal genes, with intensity of colour correlating with the proportion of genes in category annotated with that term. Purple: GO terms significantly comparatively enriched terms among Recessive lethal genes. b Comparative analysis of gene ontology between dominant and recessive among all 3187 OMIM genes. Ontology analyses is available in https://github.com/RubyDawes/GD_Informatics_Toolkit/releases/tag/v1.0.0. Highly general terms are excluded from the figure (cellular component, cell, binding etc.). Some ontology terms are abbreviated for readability. Only the 14 most significantly overrepresented categories are visualised