Figure 4.
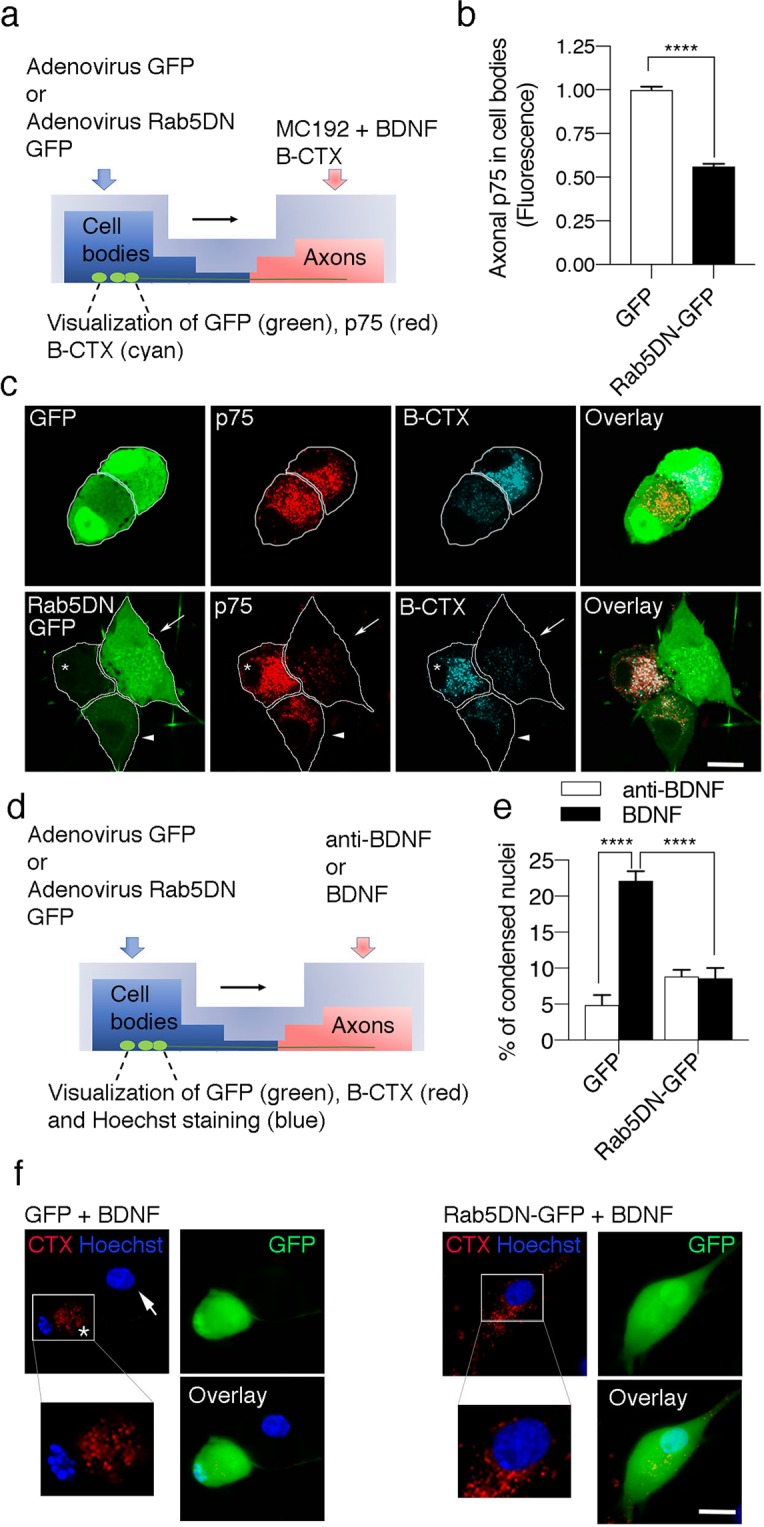
Rab5 activity is required for p75 retrograde transport and axonal BDNF-induced death signaling in sympathetic neurons. (a) Illustration of the design of the experiment used to study Rab5-dependent p75 retrograde transport and signaling in sympathetic neurons. Quantification (b) and visualization (c) of axonally labeled p75 in the cell bodies of compartmentalized sympathetic neurons. (b) Levels of axonally labeled p75 in the absence (control, GFP) or presence of a dominant negative Rab5 mutant (Rab5DN-GFP). Sixty cells from five different compartmentalized chambers were quantified. Statistically significant differences were analyzed using a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. ****p < 0,0001. (c) After 5 days in culture, sympathetic neurons were transduced with the adenovirus driving the expression of GFP (green) or a dominant negative mutant of Rab5 fused to GFP (Rab5DN-GFP, green). Twenty hours after the infection, the axon compartment was treated with BDNF, MC192-Alexa Fluor 594 (to label p75, red) and the B subunit of the cholera toxin conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647 (B-CTX, cyan) for 16 hours at 37 °C to label compartmentalized neurons. Scale bar, 10 μm. Only cells that were retrogradely labeled with B-CTX-Alexa Fluor 647 were used to quantify the retrograde transport of p75. The white arrow indicates a Rab5DN-GFP labelled neuron with reduced levels of p75. The arrowhead indicates a neuron expressing lower labels of Rab5DN-GFP when compared to the neuron labelled with a white arrow. Consistently, this neuron shows increased levels of p75. The asterisk indicates a neuron that does not express Rab5DN-GFP. This neuron expresses greater levels of p75 compared to neurons labelled with Rab5DN-GFP. (d) Illustration of the design of the experiment used to study Rab5-dependent retrograde signaling of p75 and quantify axonal BDNF-induced death signaling in sympathetic neurons. Sixty cells from seven different compartmentalized chambers were quantified at each time point. Statistically significant differences were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test. ****p < 0,0001. Only cells that were retrogradely labeled with B-CTX-Alexa Fluor 647 were used to quantify apoptosis. (e-f) Quantification (e) and visualization (f) of apoptosis of neuronal cell bodies from compartmentalized sympathetic neuronal cultures expressing GFP and Rab5DN-GFP (in green). Axons were treated with B-CTX-Alexa Fluor 647 (red) to label compartmentalized neurons. Condensed or fragmented nuclei were labeled with Hoechst (blue). The cell enclosed in a white square was magnified to enable the better visualization of the healthy or condensed nucleus labeled with an asterisk. The white arrow indicates a healthy nucleus that is not labeled with B-CTX-Alexa Fluor 647. Scale bar, 10 μm.
