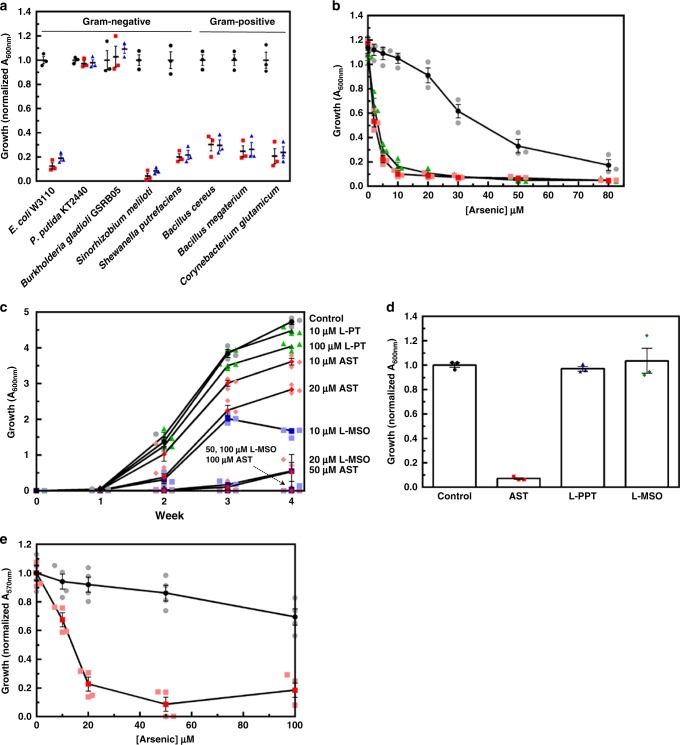
Fig. 2.
AST is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. a AST inhibits growth of both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Strains were cultured in M9 medium in the absence (black circles) or presence of 25 µM AST (red squares) or 400 µM L-PPT (blue triangles) as described in Methods, and growth was estimated from the A600nm after 24 h. Data are the mean ± SE (n = 3). b Pentavalent AST is more toxic than trivalent As(III). The toxicity of AST (triangles) was compared with MAs(III) (squares) and As(III) (circles) in E. coli AW3110 grown in M9 medium. Growth was estimated from A600nm after 24 h. Data are the mean ± SE (n = 3). Dark- and light-colored symbols represent means and individual data points, respectively. c Effect of AST on mycobacterial growth. Cultures of M. bovis BCG were inoculated at an initial density of 105 cells/ml and then incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere for up to 4 weeks in the absence (Control, circles) or presence of the indicated concentrations of GS inhibitors L-MSO (squares), L-PPT (triangles) or AST (diamonds). Growth was estimated from A600nm. Data are the mean ± SE (n = 3). Dark- and light-colored symbols represent means and individual data points, respectively. d Effect of AST on carbapenem-resistant E. cloacae. Cells were cultured in M9 medium in the absence (Control) or presence of 25 µM AST, L-PPT or L-MSO, with growth estimated from the A600nm after 24 h. Data are the mean ± SE (n = 3). e Cytotoxicity of AST in human monocytes. Human THP-1 cells were incubated in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of As(III) (circles) or AST (squares) for 24 h, and viability was determined using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl) 2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay, as described in Methods. Data are the mean ± SE (n = 4). Dark- and light-colored symbols represent means and individual data points, respectively