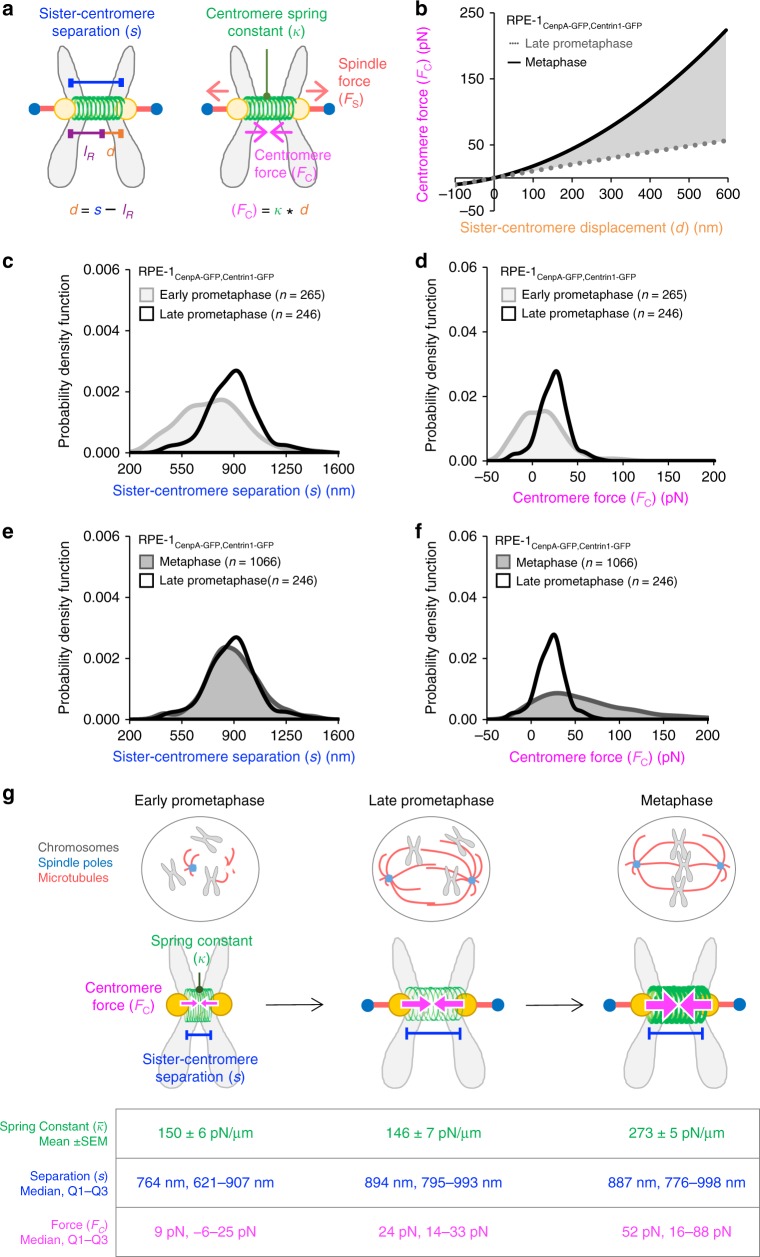
Fig. 5.
Displacement-dependent centromere-spring amplifies metaphase tension. a Schematic representation of centromere force during mitosis. During mitosis, the distance separating sister centromeres (s) is equal to their rest length plus the displacement (d) created by the external spindle force (FS). Displacement of the sister centromeres creates an internal, inward-directed centromere force FC. b The dynamic range in force transmission for a late-prometaphase chromosome (dotted gray line) versus a metaphase chromosome (solid black line) in RPE-1 cells. Centromere force at each stage was calculated using the displacement-specific spring constant (Fig. 4e–g) over the range of observed displacement values. The shaded region reflects the increase in dynamic range (+250.7%) between late-prometaphase and metaphase. c, d Probability density functions for individual observations of c sister centromere separation (s) and d centromere force (FC) at early-prometaphase (light gray line, shaded area) and late-prometaphase (black line) for RPE-1 cells (early-prometaphase: chromosomes = 265, cells = 44; late-prometaphase: chromosomes = 246, cells = 47; metaphase: chromosomes = 1066, cells = 95). e, f Probability density functions for individual observations of e sister centromere separation (s) and f centromere force (FC) at late-prometaphase (black line) and metaphase (dark gray line, shaded area) for RPE-1 cells. g Schematic illustrating centromere mechanical maturation. Left: At early-prometaphase, the centromere-spring is mechanically soft, sister centromere separation is low, and tension is also low. Center: At late-prometaphase, the mechanical stiffness of the centromere-spring is unchanged, but sister centromere separation increases substantially, which raises the median tension and narrows the range. Right: At metaphase, while sister centromere separation is similar to that in late-prometaphase, the stiffness of centromere-spring becomes displacement-dependent, thus amplifying both the magnitude and the range of the tension signal. The mean spring constant at each stage is taken from Fig. 2b. The median and IQR for sister centromere separation and centromere force were calculated from the distributions shown in Fig. 4c–f