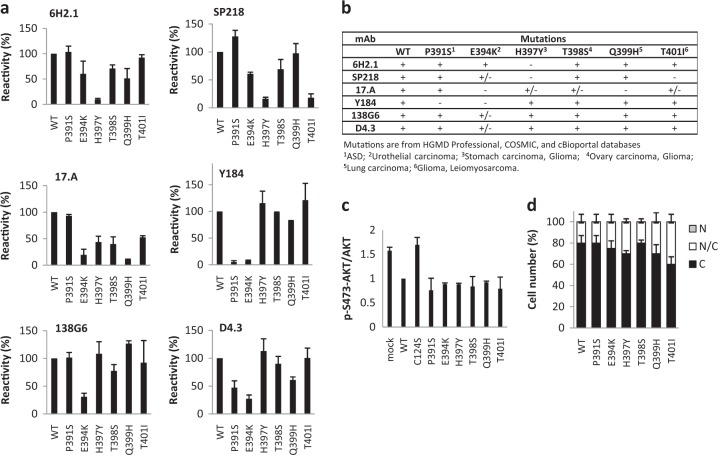
Fig. 4.
Recognition by anti-PTEN mAb and functional properties of disease-associated PTEN C-terminal tail variants. a Reactivity of anti-PTEN mAb with amino acid substitutions at PTEN C-terminus found in tumors or in patients. Quantification of the reactivity is shown (mean ± s.d. from two independent experiments), as in Fig. 3c. b Summary of the reactivity of the different anti-PTEN mAb with amino acid substitutions found in tumors or in patients mutations. +, binding; +/− diminished binding; -, no binding. c Functional activity of the disease-associated PTEN variants. Data are shown as the ratio pSer473-AKT/AKT (mean ± s.d. from two independent experiments), quantified by immunoblot with anti-pSer473-AKT and anti-AKT antibodies, from lysates from COS-7 cells co-transfected with PTEN and AKT1. d Subcellular localization of disease-associated PTEN variants. Data are shown as the percentage of cells displaying cytoplasmic (C), nuclear/cytoplasmic (N/C), or nuclear (N) localization (mean ± s.d. from two independent experiments)