Fig. 6.
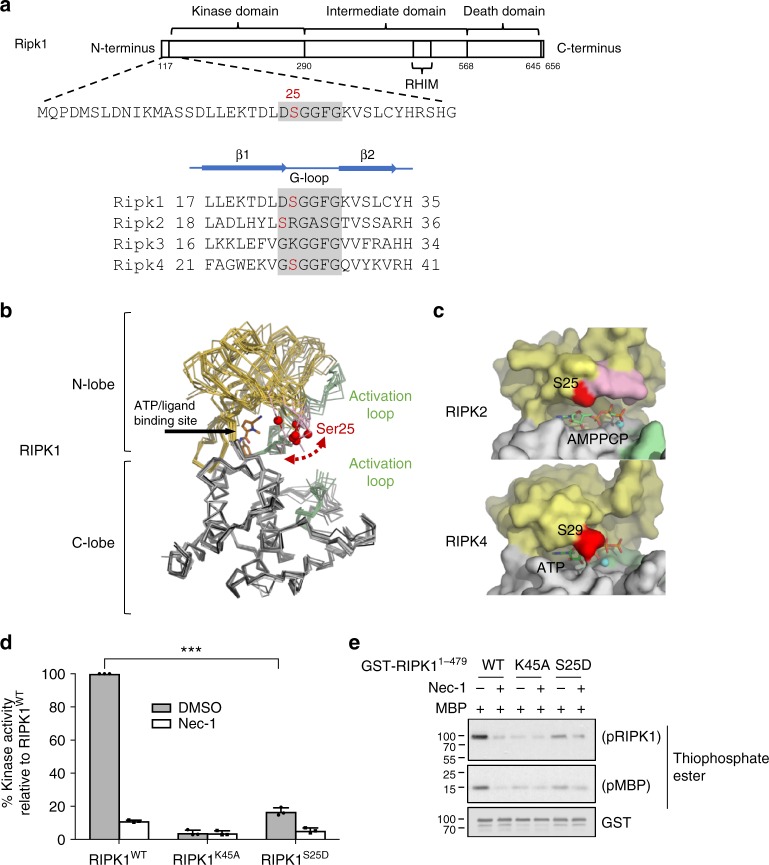
Phospho-Ser25 directly inhibits RIPK1 catalytic activity. a Schematic representation of mouse RIPK1 primary structure and excerpts from structure-based sequence alignments for murine RIPK1–4 (Uniprot sequences Q60855, P58801, Q9QZL0, Q9ERK0) focusing on the region of Ser25. b Ser25 localizes in the flexible Glycine-rich loop covering the RIPK1 nucleotide binding site. Structural overlays were carried out with respect to the C-lobe of RIPK1 in complex with necrostatin-4 (pdb entry 4ITJ) and employed all available RIPK1 kinase domain structures (pdb entries 4ITH, 4ITI, 4NEU, 5HX6, 5TX5, 4M66, 4M69). The red spheres correspond to the C-alpha positions of Ser25 in the different structures. The structurally ordered parts the activation loop are drawn in green. The intervening portion of the activation loop is disordered in all crystal structures of RIPK1 to date. c Structures of human RIPK2 in complex with the non-hydrolyzable ATP analog AMP-PCP and RIPK4 in complex with ATP. d, e In vitro kinase assays using recombinant truncated RIPK1 mutants (AA 1–479). d Quantitative kinase activity measured by ATP consumption using the ADP-Glo kinase assay. Results are presented as a percentage relative to the kinase activity in the wild-type protein and is the mean ± SEM of three independent kinase assays (n = 3). e Qualitative kinase activity monitored by immunoblot and revealing RIPK1 autophosphorylation and RIPK1-mediated phosphorylation of MBP