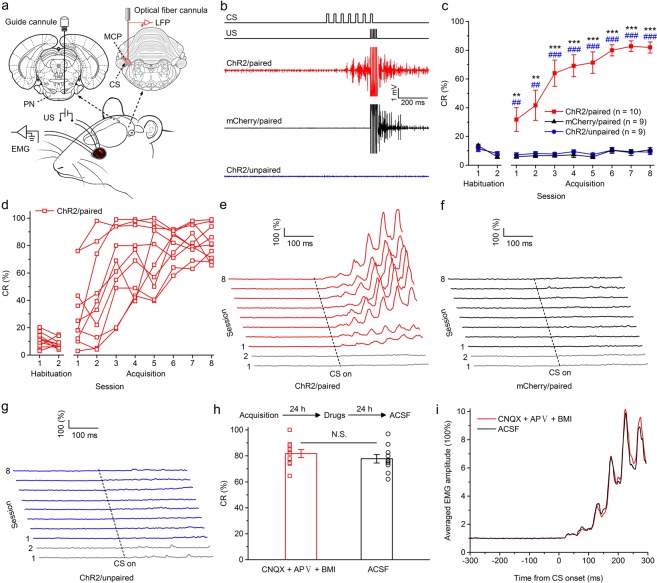
Figure 2.
Optogenetic stimulation of mossy fibers in the left MCP as a CS is sufficient for the acquisition of the DEC. (a) Behavioral diagram. Rats with virus injection were implanted with 4 electrodes into the upper left eyelid for delivery of the US and for recording the EMG activity of the left O.O. muscle. Moreover, an optrode was targeted into the left MCP for optical stimulation and recording LFP. A guide cannula was implanted into the right PN for drug injection. (b) Upper panel: the delay conditioning paradigm illustrating the timing of the CS and US. Below panel: the representative O.O. EMG of the ChR2/paired, mCherry/paired, and ChR2/unpaired groups on the 8th conditioning session. (c) Average CR% for the ChR2/paired, mCherry/paired, and ChR2/unpaired groups (* and # indicate significant differences between the ChR2/paired group and mCherry/paired and the ChR2/unpaired groups; ** or ##P < 0.01, *** or ###P < 0.001; 2-way ANOVA with repeated measures followed by Tukey post hoc test). (d) Individual learning curves of rats in ChR2/paired group. (e–g) EMG response topographies across two habituation and eight acquisition training sessions in ChR2/paired (e), mCherry/paired (f), and ChR2/unpaired (g) groups. (h) CNQX, APV, and BMI administration did not affect the CR% of ten learned rats (N.S., not significant, 2-tailed paired Student’s t-test). (i) The EMG response topographies for CNQX, APV, and BMI infusion or ACSF infusion were shown. Data are represented as mean ± s.e.m.