Fig. 2.
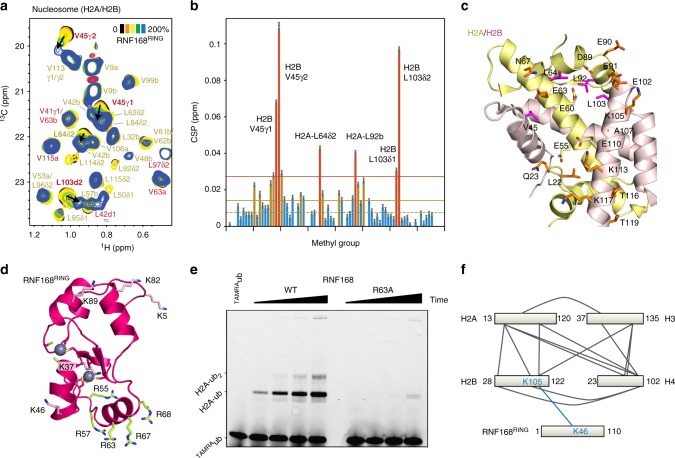
RNF168RING binds the nucleosome acidic patch using its Arg-rich helix. a Section of the 2D 1H-13C methyl-TROSY spectrum of the nucleosome with ILV-labeled H2A/H2B with increasing amounts of RNF168RING added. Color coding indicated. Labels a/b refer to either of the δ1/δ2 Leu or γ1/γ2 Val methyl groups. b Weighted chemical shift perturbation (CSPs) between the spectra of 1:2 and 1:0 nucleosome:RNF168RING. Residues with CSPs that are one (two) standard deviations larger than the 10% trimmed mean are highlighted in yellow (red) and labeled. Error bars are s.d. based on 1 ppb standard error in peak position in 1H and 13C dimension. c The RNF168 binding surface as defined by NMR (shown as sticks, color coded in orange/magenta for dimer/nucleosome data). Side chains of other acidic patch residues are shown as sticks, color coded in yellow for H2A and light red for H2B. d Crystal structure of the RNF168RING domain with Arg residues of the basic-helix highlighted as yellow sticks. Lysine residues are shown as sticks and labeled, Zn atoms shown as spheres, coordinating residues as sticks. e Nucleosome ubiquitination by either wild-type (WT) or R63A mutant RNF168RING. Fluorescent TAMRA-labeled ubiquitin was used to detect ubiquitinated species. Samples were resolved using SDS-PAGE. For both wild-type and mutant time points were taken at 5, 15, 30 and 60 min of incubation of the reaction mixture. Molecular size of mono- and di-ubiquitinated H2A is indicated. f Schematic representation of inter-histone crosslinks (gray; for rigid histone core only) and intermolecular RNF168-nucleosome crosslinks (blue) obtained from XL-MS. Source data are provided as a Source Data file