Fig. 3.
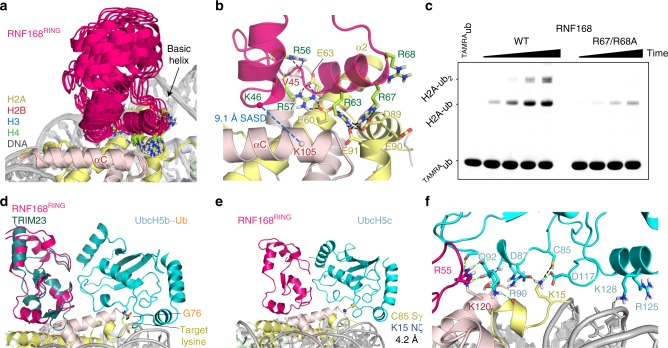
Structure of the RNF168RING–nucleosome complex and implications for E2 positioning. a Superposition of the 10 best scoring solutions of cluster 1 (containing 187 out of 200 solutions) calculated using HADDOCK. Color coding indicated. Docking statistics are reported in Supplementary Fig. 4. b Zoom on the binding interface for the best scoring solutions of cluster 1, with key hydrogen-bond interactions involving the Arg-rich helix indicated. The Cα atoms and SASD of the crosslinked residues is indicated. c Nucleosome ubiquitination by either wild-type (WT) or R67/R68A mutant RNF168RING. Fluorescent TAMRA-labeled ubiquitin was used to detect ubiquitinated species. Samples were resolved using SDS-PAGE. For both wild-type and mutant time points were taken at 2, 6, 18, and 40 min of incubation of the reaction mixture. Molecular size of mono- and di-ubiquitinated H2A is indicated. d Superposition of the TRIM23 E3 complex with Ub-conjugated E2 (PDB-ID 5VZW) and the RNF168RING-nucleosome structure, showing close approximation of the Ub C-terminal residue G76 in the active site to the target lysine. e Structural model of the ternary UbcH5c-RNF168RING-nucleosome complex calculated using HADDOCK. The best scoring solution is shown, distance between the E2 active site and target lysine is indicated. f Zoom on the UbcH5c-nucleosome interface showing hydrogen bonds with green dashes. Panels (e and f) show models with human histones, residues are numbered accordingly. Source data are provided as a Source Data file