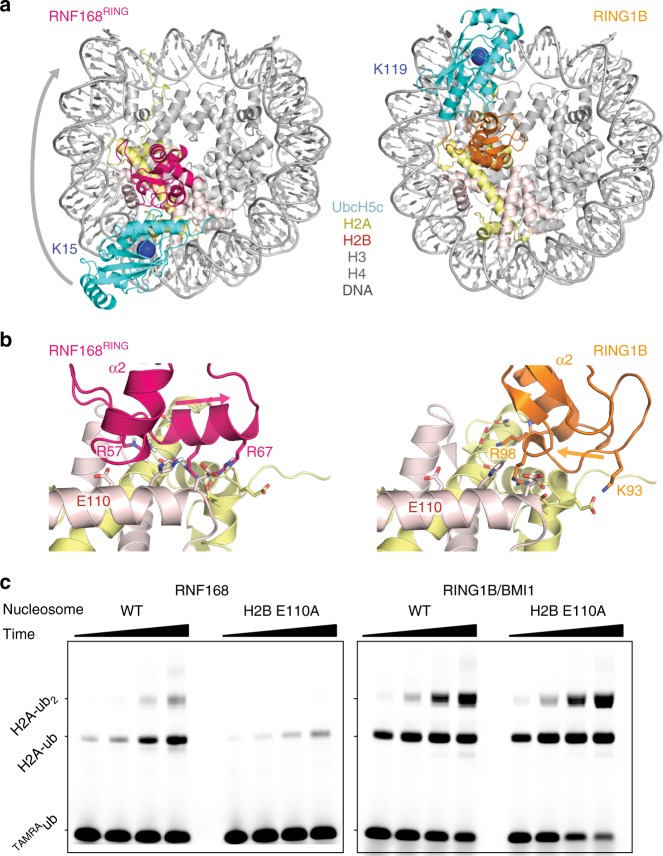
Fig. 4.
Uncoupling of PRC1 and RNF168 ubiquitination. a Top view on the nucleosome highlighting the 180° rotated position of UbcH5c in the RNF168 (left) compared to RING1B nucleosome complex (right). Color coding indicated in the Figure, position of the target lysines is indicated with the blue sphere. b Side-by-side comparison of the RING domain positions on the acidic patch, RNF168 (right) and RING1B (left). Secondary structure elements are labeled to highlight the approximate 180° turn of the RING domain, also indicated by the arrow. The H2B E110 (E113 in humans) side chain is close to the E3 RING surface for RNF168 but far from the surface of RING1B. Selected side chains are shown as sticks. c Nucleosome ubiquitination by either RNF168RING or RING1B/BMI1 on wild-type (WT) or H2B E110A nucleosomes. Fluorescent TAMRA-labeled ubiquitin was used to detect ubiquitinated species. Samples were resolved using SDS-PAGE. For all samples time points were taken at 2, 6, 18, and 40 min of incubation of the reaction mixture. Molecular size of mono- and di-ubiquitinated H2A is indicated. Source data are provided as a Source Data file