Figure 2. PARP-specific identification of target proteins and ADP-ribosylation sites using asPARPs and a clickable NAD+ analog.
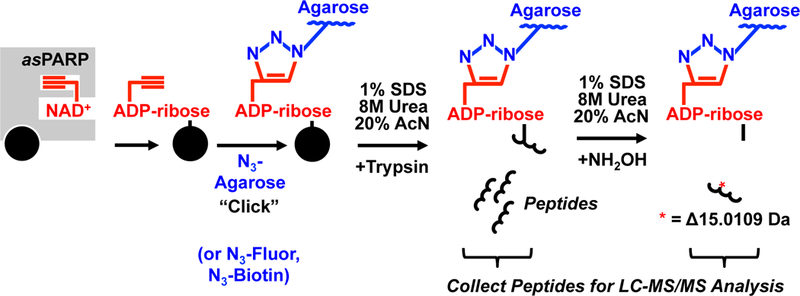
Schematic representation of the asPARP methodology used to determine aspartate and glutamate amino acids ADP-ribosylated by an specific PARP family member. In this approach, an asPARP protein (grey square) uses the alkyne group-containing NAD+ analog 8-Bu(3-yne)T-NAD+ (shown in red) to catalyze transfer of 8-Bu(3-yne)T-ADP-ribose (also shown in red) onto a target protein (black circle). The alkyne group of 8-Bu(3-yne)T-ADP-ribose is used to covalently conjugate the PARP target protein to azido-agarose resin (N3-Agarose) (shown in blue) through the use of an orthogonal copper-catalyzed cycloaddition reaction, also known as “click” chemistry. Following conjugation, the resin is washed thoroughly with different strong denaturants and subjected to trypsinization to release unconjugated peptides of PARP target proteins, which can be collected and analyzed by LC-MS/MS analysis. After trypsinization, the resin is washed thoroughly again and treated with hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to release the conjugated peptides. The released conjugated peptides will exhibit a molecular weight change of 15.0109 Daltons and a signature m/z shift, which can be used to determine the specific site of ADP-ribosylation by mass spectrometry.
