Figure 3. Examples of asPARP-1-dependent labeling of proteins and in-gel fluorescence analyses.
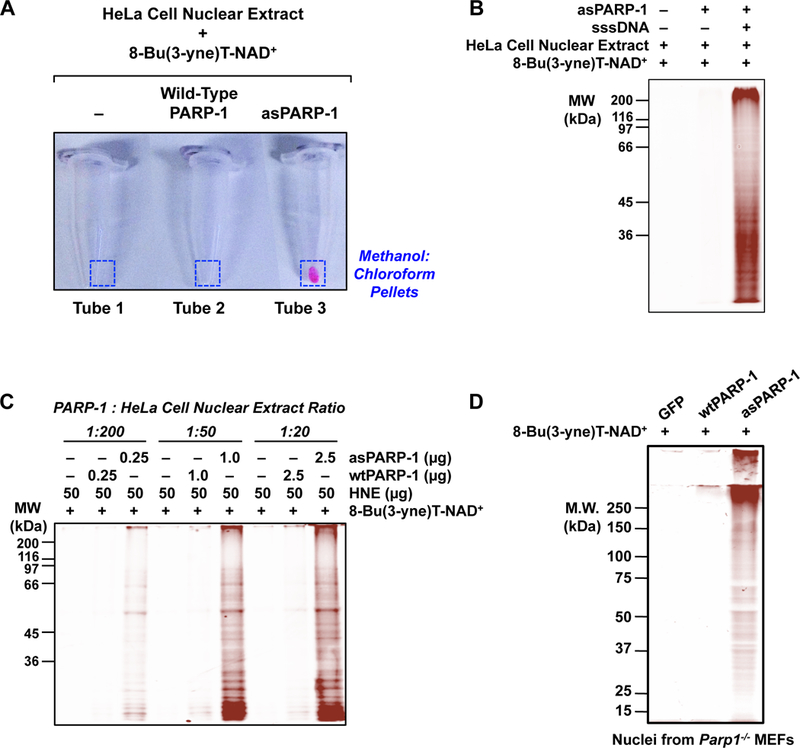
(A) An example of fluor incorporation into methanol:chloroform extracted protein pellets following bio-orthogonal conjugation of 8-Bu(3-yne)T-ADP-ribosylated proteins with azido-TAMRA dye. Only the combination of asPARP-1, 8-Bu(3-yne)T-NAD+, and HeLa cell nuclear extract proteins yields a detectable fluor-labeled product.
(B) An example of DNA- and asPARP-1-dependent 8-Bu(3-yne)T-ADP-ribosylation of HeLa cell nuclear extract proteins, with subsequent visualization of the PARP-1 target proteins by ingel fluorescence. The 8-Bu(3-yne)T-ADP-ribosylated proteins were visualized by bio-orthogonal conjugation with azido-TAMRA dye following separation by SDS-PAGE. Sheared salmon sperm DNA (sssDNA) was added to activate the asPARP-1 catalytic activity. Molecular weight markers (in kiloDaltons) are shown.
(C) The assay shown is similar to the one shown in (B), except that different mass ratios of PARP-1 protein to HeLa cell nuclear extract protein were used: 1:200, 1:50, or 1:20. Wild-type PARP-1 (wtPARP-1) or analog-sensitive PARP-1 (asPARP-1) proteins were mixed with HeLa cell nuclear extract protein in the ratios specified and incubated with 8-Bu(3-yne)T-NAD+. The 8-Bu(3-yne)T-ADP-ribosylated proteins were visualized by bio-orthogonal conjugation with azido-TAMRA dye following separation by SDS-PAGE. Sheared salmon sperm DNA (sssDNA) was added to each reaction to activate the asPARP-1 catalytic activity. Molecular weight markers (in kiloDaltons) are shown.
(D) Intact nuclei isolated from PARP-1 knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts (Parp1−/− MEFs) with ectopic expression of GFP (as a control), wild-type PARP-1 (wtPARP-1), or analog-sensitive PARP-1 (asPARP-1), were incubated with 250 µM 8-Bu(3-yne)T-NAD+ to stimulate asPARP-1-mediated ADP-ribosylation. The 8-Bu(3-yne)T-ADP-ribose-labeled nuclear proteins were then clicked to azido-rhodamine, extracted with methanol:chloroform, and separated by SDS-PAGE. The gel was analyzed on a fluorescence imager.
