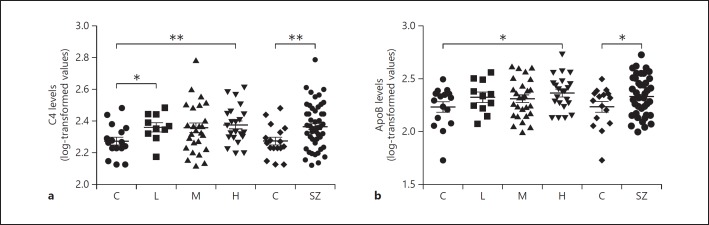
Fig. 2.
log-transformed relative data for levels of C4 (a) and ApoB (b) in controls (C; n = 20) and patients with schizophrenia (SZ; n = 60) undergoing treatment with antipsychotics conferring a low (L; n = 11), medium (M; n = 27), or high (H; n = 22) risk for developing metabolic syndrome. The data were assessed by Student's t test comparing the controls with each group separately. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.