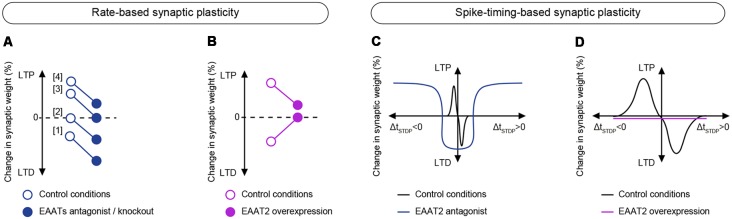
Figure 3.
Effects of EAATs modulation on long-term plasticity. (A,B) Effects of EAATs regulation on rate-based plasticity. (A) Downregulation of EAATs by pharmacological inhibition or genetic knock-out (closed circles) results in a lower threshold for LTD induction and a higher threshold for LTP induction using rate-based plasticity paradigms compared to control conditions (open circles). Pharmacological inhibition of EAATs: (1) increases LTD magnitude (Brasnjo and Otis, 2001); (2) promotes LTD (Massey et al., 2004; Wong et al., 2007); (3) prevents LTP induction (Wang et al., 2006). Genetic knock-out of EAATs; and (4) decreases LTP amplitude (Katagiri et al., 2001; Scimemi et al., 2009). (B) Upregulation of EAATs by chronic ceftriaxone treatment (closed circles) prevents the expression of LFS-induced LTD and decreases the amplitude of HFS-induced LTP compared to control conditions (open circles; Omrani et al., 2009). (C,D) Effects of EAATs regulation on spike-timing-based plasticity. (C) Downregulation of EAAT2 by pharmacological inhibition with DHK results in a broadening of the permissive window (ΔtSTDP) for plasticity expression (Valtcheva and Venance, 2016). (D) Upregulation of EAATs by chronic ceftriaxone treatment prevents the expression of STDP (Valtcheva and Venance, 2016).