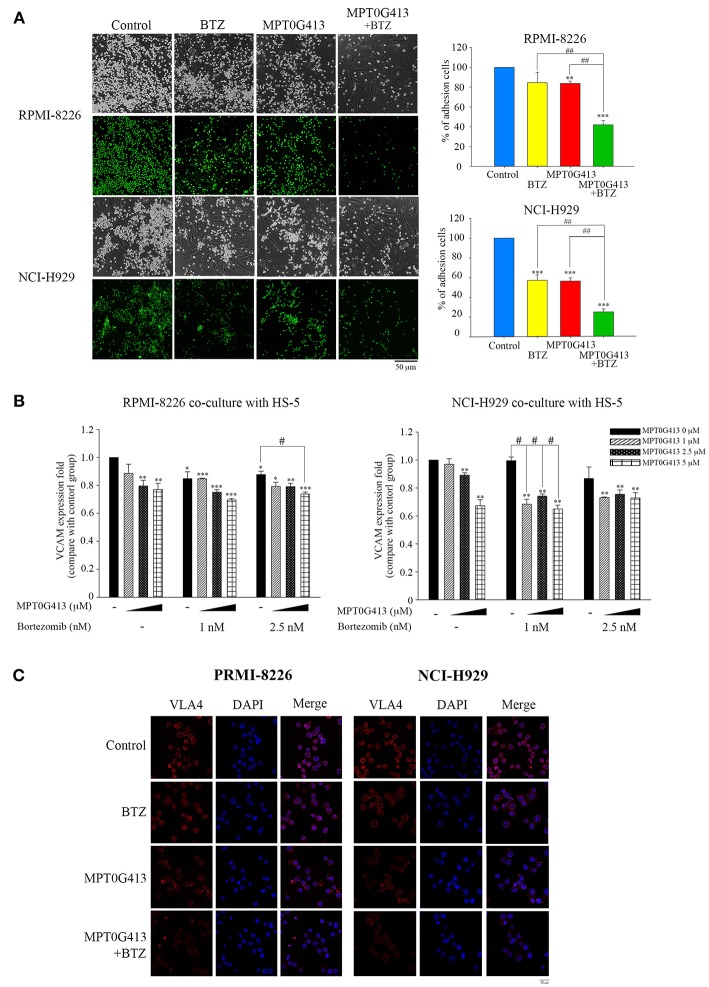
Figure 5.
A combination of MPT0G413 and bortezomib inhibited the adhesion of multiple myeloma cells to bone marrow stromal cells. (A) RPMI-8226 and NCI-H929 multiple myeloma cells were treated with MPT0G413 (2.5 μM), bortezomib (2.5 nM), or both agents for 24 h and subsequently labeled with 10 μM BCECF-AM. The labeled cells were subsequently co-cultured with HS-5 bone marrow stromal cells for 2 h. After incubation, non-adherent cells were removed by gentle washing with phosphate-buffered saline, and adherent multiple myeloma cells were, respectively photographed by light and fluorescence microscopy. Images depict 40 × magnification (Scale bar = 50 μm). Image J software was used to quantify the fluorescence microscopy images. (B) Multiple myeloma cells were co-cultured with HS-5 cells and incubated with MPT0G413 (2.5 μM), bortezomib (2.5 nM), or a combination of both agents for 24 h. The expression of VCAM-1 was measured by ELISA as described in the Materials and Methods. Results represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 compared with the control group. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 compared with the relevant control group. (C) RPMI-8226 and NCI-H929 cells were treated with MPT0G413 (2.5 μM), bortezomib (2.5 nM), or combination therapy for 6 h. Subsequently, the samples were stained with anti-VLA4 (red) and DAPI (blue) prior to a confocal microscopy analysis. Scale bar = 20 μm.