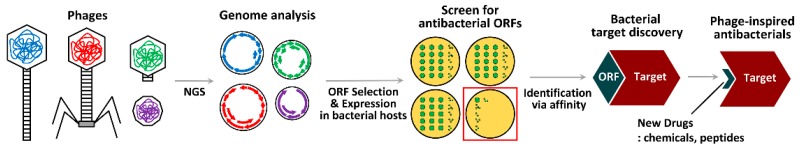
Figure 4.
Work flow of phage-inspired antibacterial design. Once phages with strong antibacterial activity are identified, their whole genomes are sequenced and analyzed for open reading frame (ORF) selection. The selected ORFs are expressed in target bacterial hosts to screen for antibacterial activity based on growth or virulence inhibition. Then, the gene product of an ORF hit (dark green) is exploited to fish out the host target based on protein–protein interactions. The discovered host target, the phage-inspired bacterial target, serves as a molecular scaffold for new drug screening. Finally, chemicals or peptides that bind to the host target can be isolated and further developed as phage-inspired antibacterials.