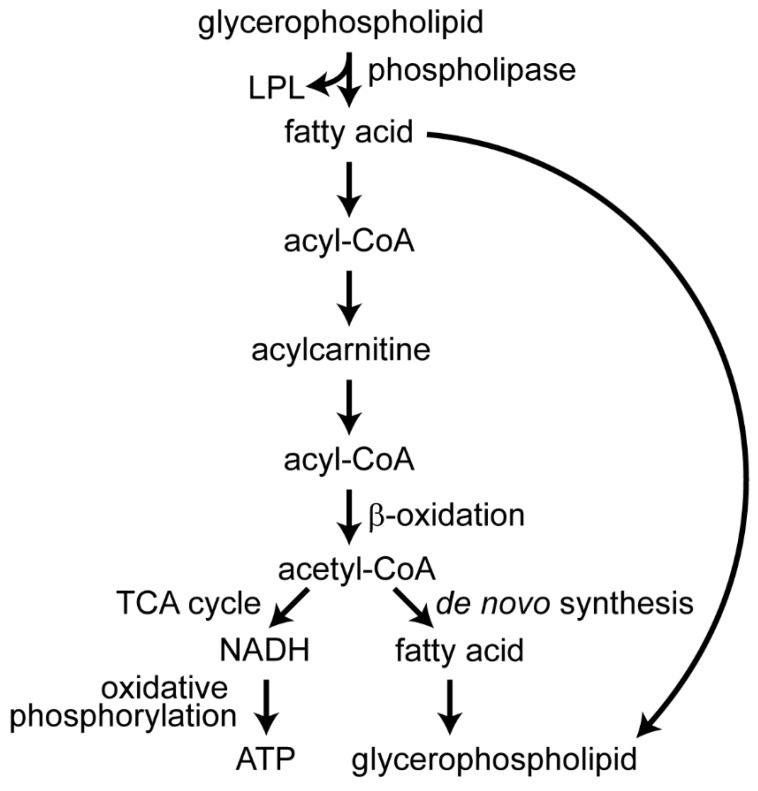
Figure 3.
Fatty acid metabolism. Fatty acids are freed from glycerophospholipids by phospholipases producing lysophospholipids (LPL). Fatty acids are then conjugated to coenzyme A (CoA). The fatty acyl is bonded to carnitine for transport to the mitochondrial matrix, where they can undergo β-oxidation generating acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA can enter the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to generate NADH which will produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) during oxidative phosphorylation, or the acetyl-CoA can be used to build new fatty acids and glycerophospholipids. The fatty acids can also be used to remodel glycerophospholipids in the Lands’ cycle without being degraded [98].