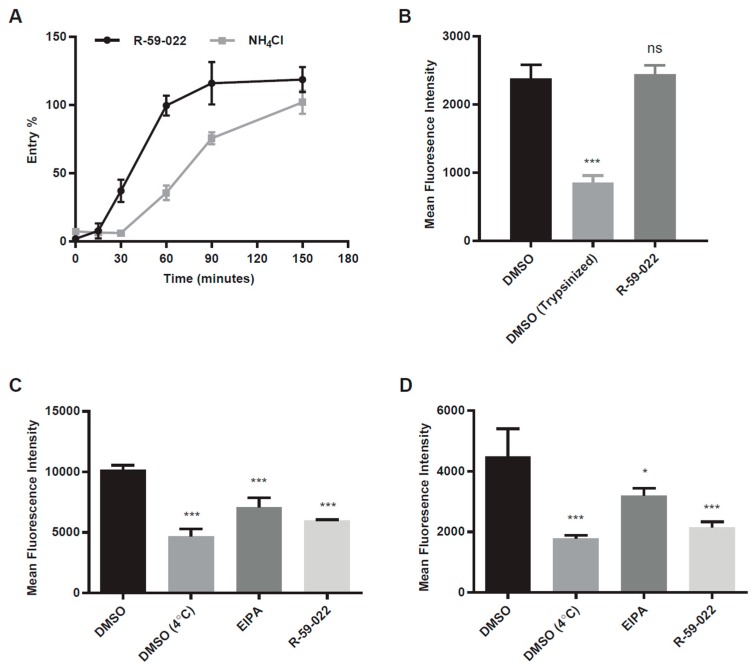
Figure 3.
R-59-022 blocks internalization of EBOV VLPs into the host cell. (A) Time of addition assay in Vero cells with βlam VLPs harboring EBOV GP. Cells were infected at t = 0 and R-59-022 (5 µM) or NH4Cl (15 mM) were added at indicated time points post-infection. Viral entry was measured by determining the percentage of cells with cleaved CCF2 compared to vehicle; (B) Attachment assay in Vero cells using mCherry VLPs harbouring EBOV GP. Vero cells were pre-treated with 5 µM R-59-022 or vehicle followed by a 1-hour incubation at 4 °C with EBOV VLPs. One set of DMSO samples was trypsinized to remove bound VLPs. Fluorescence of mCherry VLPs was measured by flow cytometry and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for each sample determined using the FlowJo software; (C,D) Internalization assay in (C) Vero cells and (D) BMDMs using mCherry EBOV VLPs. Cells were pre-treated with 5 µM R-59-022, 30 µM EIPA, or vehicle followed by addition of VLPs and spinoculation at 4 °C. Cells were washed with cold PBS and pre-warmed media containing inhibitor or vehicle was added. Cells with attached VLPs were incubated at 37 °C for 1 h to allow for internalization and were then moved to 4 °C for 15 min. Cells were then trypsinized at 4 °C for 30 min to remove non-internalized VLPs. Fluorescence of internalized mCherry VLPs was measured by flow cytometry and mean fluorescence intensity determined using the FlowJo software. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns: not significant.