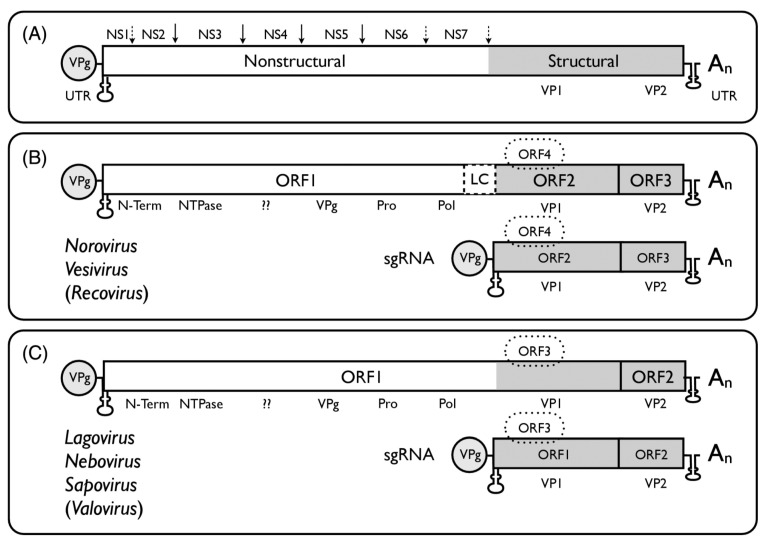
Figure 1.
Schematic genome organization of viruses in different genera of the Caliciviridae. (A) The long ORF encodes a polyprotein consisting of seven mostly non-structural proteins (ORF1) and 2–3 structural proteins (ORF2–ORF4). (B) NS3 encodes an NTPase, NS5 the VPg (a structural protein), NS6 a protease, NS7 the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). NS1, NS2 (NS1 + NS2 are also called N-Term), and NS4 have functions in the formation of membranes of the viral replication sites and interact with proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum [32,33]. (C) For Norovirus and Vesivirus ORF2 encodes the major structural protein VP1 (for Vesivirus including a precursor N-terminal leader protein (LC). For Sapovirus, Lagovirus, and Nebovirus the VP1 is derived from the C-terminus of ORF1. ORF2 or ORF3 encode VP2, and ORF4 encodes a protein which has been identified as virulence factor 1 (VF1) for MuNoV. The Nacovirus [28,29], Minovirus [31], and Salovirus [30] genomes have structures as shown in panel C for Lagovirus, Nebovirus, Sapovirus, and Valovirus. From references [24,28,29,30,31], with permission of authors and publisher.