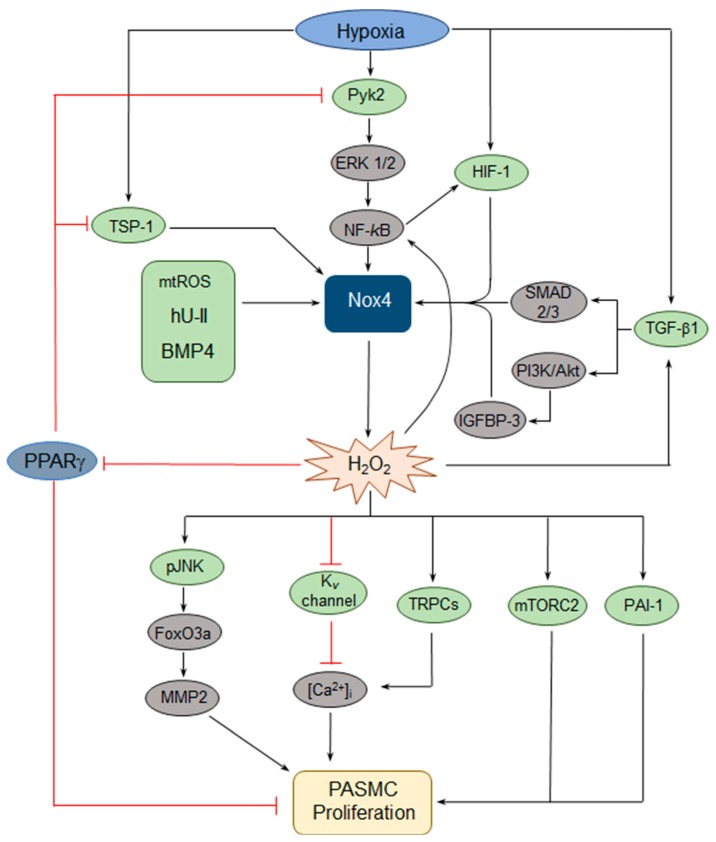
Figure 2.
Schematic of key pathways involved in Nox4-mediated effects on pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell (PASMC) proliferation. Hypoxia upregulates Nox4 via several pathways, including a proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK 1/2)-nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) axis, hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1 (HIF-1), transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), and thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1). Other activators of Nox4 include human urotensin II (hU-II), bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4), and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS). Importantly, several of these pathways include feed-forward loops, some of which feature peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) as a key component. Downstream effectors of Nox4-derived hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) include phosphorylated c-Jun-NH(2)-terminal kinase (pJNK), mammalian target of rapamycin 2 (mTORC2), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), and multiple pathways that increase intracellular calcium ([Ca2+]i). PI3K = phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt = protein kinase B; IGFBP-3 = insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3; FoxO3a = Forkhead Box O3a; MMP2 = matrix metalloproteinase 2; Kv = voltage-gated potassium; TRPC = transient receptor potential channel.