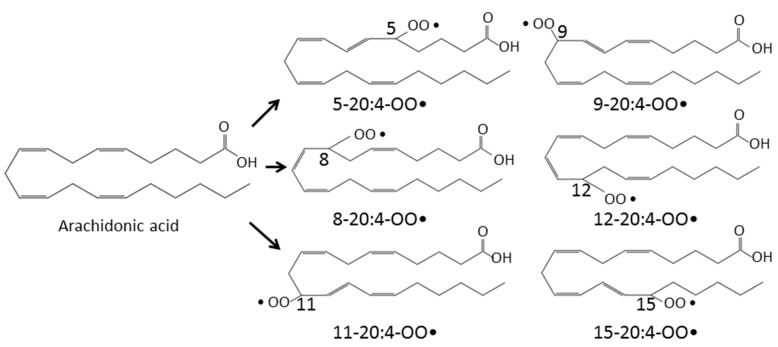
Figure 2.
Formation of various arachidonic acid hydroperoxides. As described in Figure 1, abstraction of the bis-allylic hydrogen attached to the –C– atom at position 7 leads to the formation of arachidonic acid peroxides (5-20:4-OO• or 9-20:4-OO•). Abstraction of the bis-allylic hydrogen at position 10 and 13 generates arachidonic acid hydroperoxides (8-20:4-OO• or 12-20:4-OO•) and hydroperoxides (11-20:4-OO• or 15-20:4-OO•), respectively. Arachidonic acid hydroperoxides (5-20:4-OOH and 15-20:4-OOH) are generated from arachidonic acid peroxides (5-20:4-OO• and 15-20:4-OO•), respectively. On the other hand, arachidonic acid peroxides (8-20:4-OO•, 9-20:4-OO•, 11-20:4-OOH and 12-20:4-OO•) are converted to their corresponding endoperoxides, respectively.