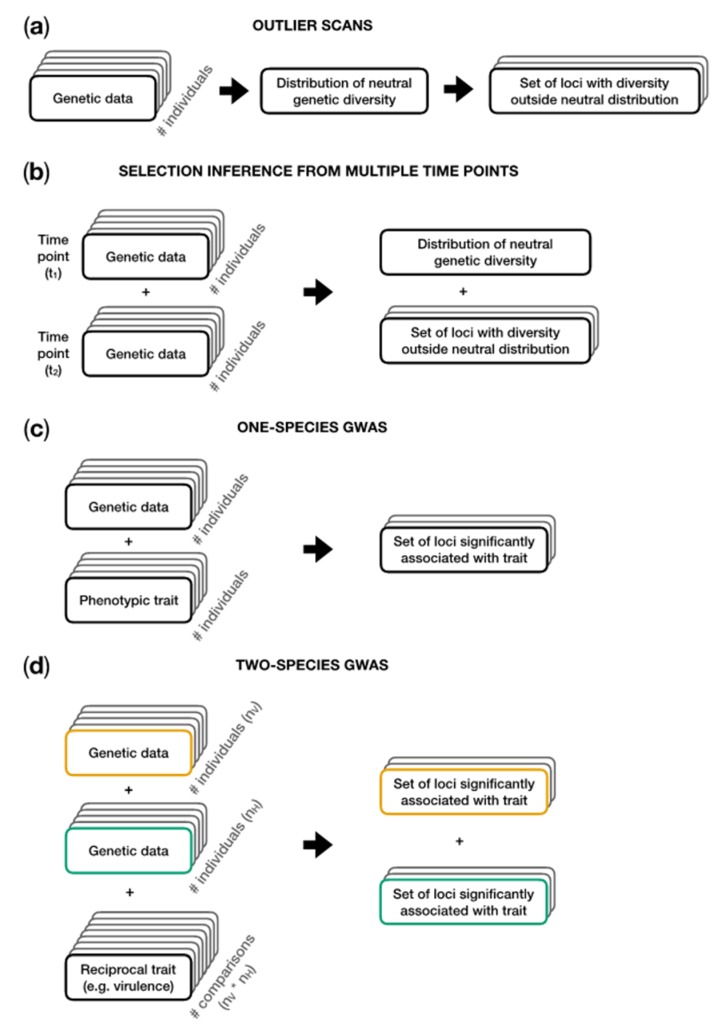
Figure 4.
Analysis steps involved in the genetic inference methods outlined in Section 5. (a) In outlier scans, genetic data are used to obtain an estimate of the demographic history and the distribution of neutral diversity given this demography. Loci which are at the extremes or even outside of this neutral distribution are subsequently identified as putatively under selection. (b) Genetic data from multiple time points allow the calculation of changes in allele frequencies over time. This increases the power to jointly estimate the demography and identify loci under selection. (c) Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are performed with phenotypic and genetic information from a sample of individuals within a population to detect associations between genetic variants and a certain phenotype (e.g., quantitative virulence). (d) Two-species GWAS integrates genomic information from a sample of nH host individuals and nV virus individuals and phenotypic outcome of all nH * nV pairwise interactions. Data from the virus are shown in yellow. Data from the host are shown in green.