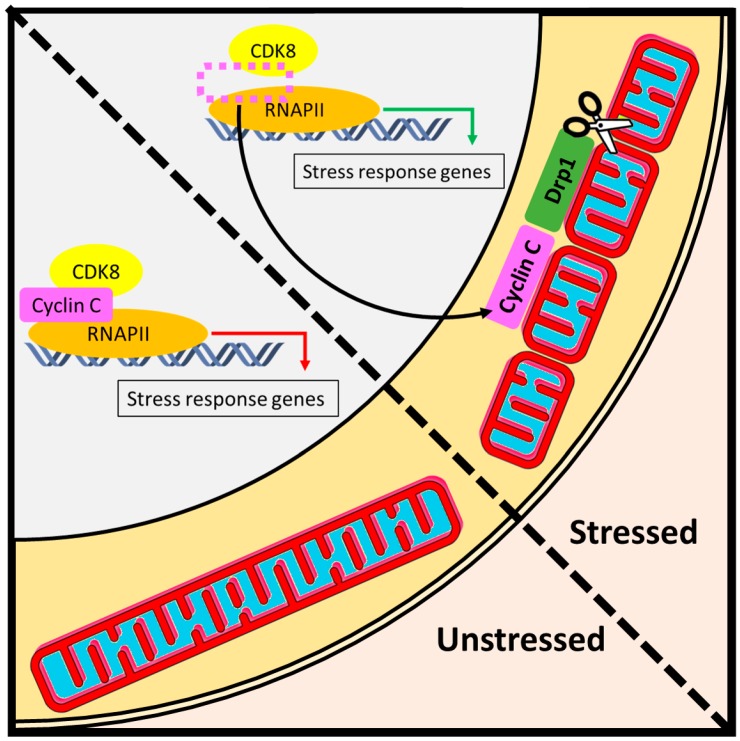
Figure 5.
Day job versus night job function of cyclin C. (Left) Under normal conditions, cyclin C performs its day job as a nuclear transcription factor that regulates RNA Pol II-dependent activity. In unstressed cells, mitochondria maintain a reticular structure [33]. (Right) The night job function of cyclin C is initiated by cellular stress and is associated with the activation of two layers of stress defense. First, under adverse conditions such as oxidative stress, a portion of cyclin C exits the nucleus to induce Drp1-dependent mitochondrial scission. The resulting fragmentation of mitochondrial network facilitates downstream stress responses such as mitophagy or apoptosis. Second, upon dissociation of cyclin C from the promoters of stress response genes, the activity of RNA Pol II is regained, which triggers a host of adaptive mechanisms such as antioxidant defense or unfolded protein response.