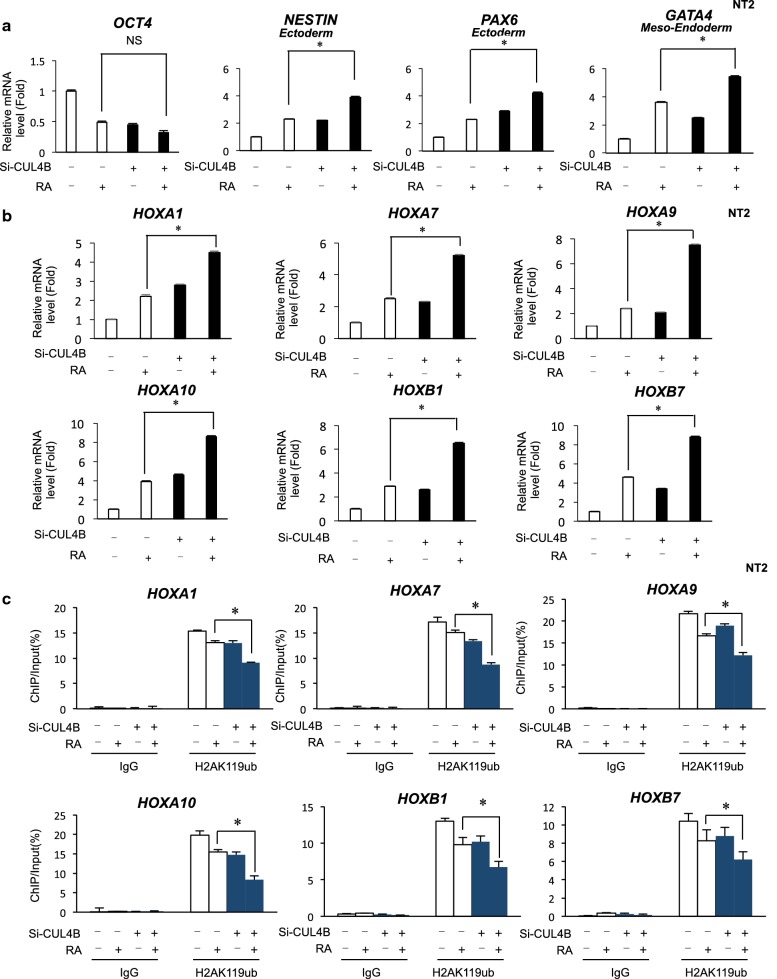
Fig. 1.
a Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showed that CUL4B loss had a positive effect on the RA-induced increases in differentiation genes mRNA levels in NT2 cells. Data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05. b Knockdown of CUL4B affected mRNA level of Hox genes in RA-induced NT2 cells. NT2 cells were knockdown of CUL4B for 24 h. Then, after 24 h of RA treatment, cells were collected and analyzed. Data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05. c Quantitative ChIP analysis was performed to analyze the effect of CUL4B loss on the RA-induced changes in H2AK119ub1 levels at the Hox genes. Enrichment of the Hox genes promoter was measured by qPCR. Data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05