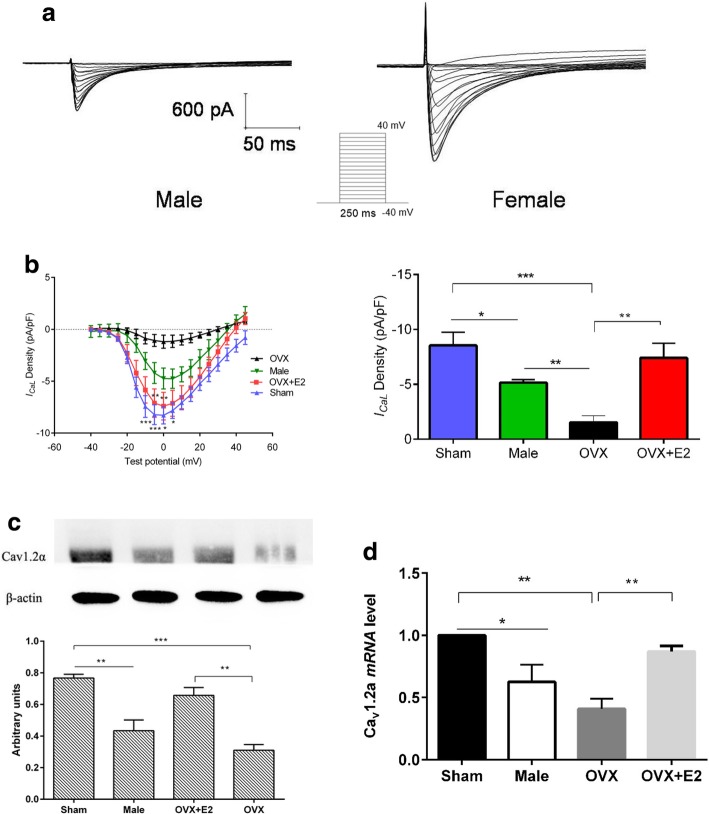
Fig. 2.
The effects of estrogen on sex differences in basal ICaL density (a), Representative voltage-clamp protocol (shown in inset) and traces of ICaL in male and female myocytes elicited by the voltage steps. b (left) current-voltage comparisons derived from the protocol shown in the inset in (a) for sham, male, OVX, and OVX + E2 myocytes. Peak ICaL density is shown on the right, (n = 6–10 cells/4 mice). All presented data are mean ± S.E.M. (c and d). Estrogen modulates sex differences in basal mRNA and protein level of the L-type Ca2+ channel. c Comparisons of L-type Ca2+ channel protein levels in sham, male, OVX, and OVX + E2. (n = 3 mice). d L-type Ca2+ channel mRNA levels in sham, male, OVX, and OVX + E2. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. All data are presented as mean ± S.E.M