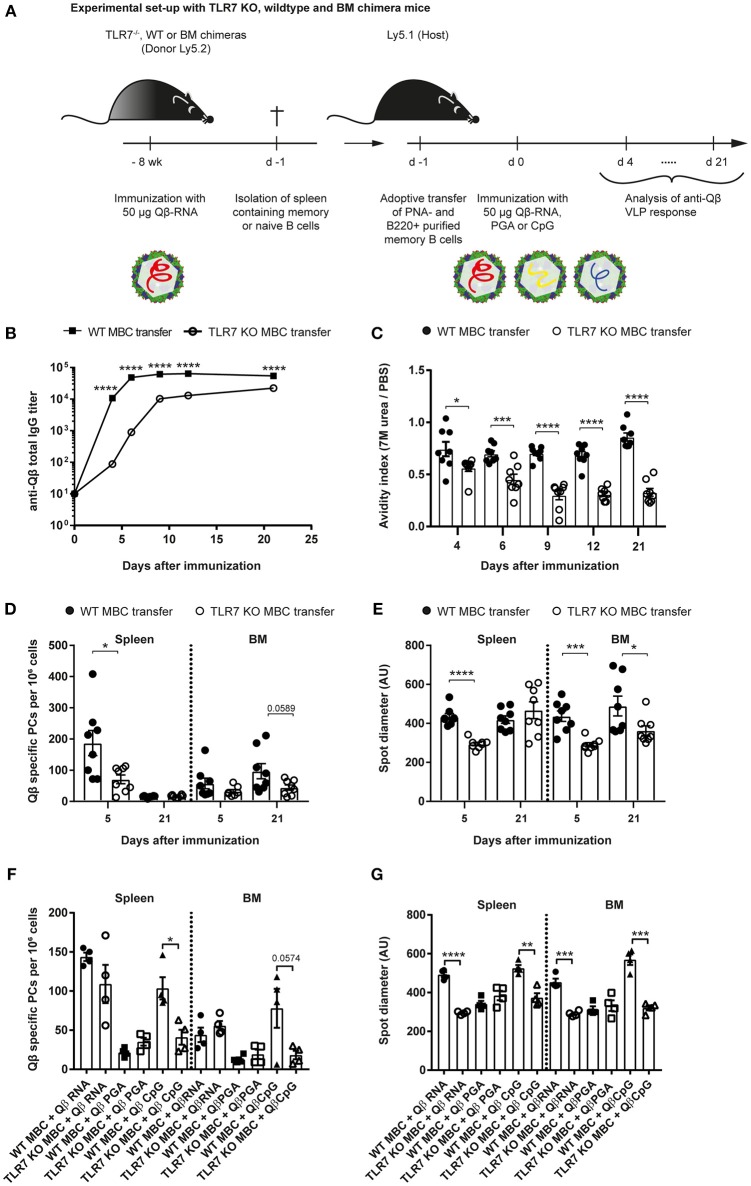
Figure 3.
TLR7 must be present during memory B cell induction to generate secondary PCs after challenge with VLPs. (A) Memory B cells were induced in TLR7 KO, WT, or BM chimeras by immunization with 50 μg Qβ-RNA i.v. Eight weeks after immunization spleens were isolated and PNA− B220+ MACS purified cells were transferred into host mice (Ly5.1). One day after the transfer, recipient mice were challenged with 50 μg Qβ-RNA (B–E) or Qβ-RNA, Qβ-PGA, and Qβ-CpG (F,G) i.v. Spleens, bone marrow, and serum were taken at several time points after challenge. (B) Qβ-specific total IgG titers after WT (black squares) or TLR7 KO (open circles) memory B cell transfer were determined by ELISA. (C) The avidity index after WT (black circles) or TLR7 KO (open circles) memory B cell transfer was determined by a modified ELISA. (D,E) ELISPOT assays were used to determine the number (D) of Qβ specific PCs and the spot diameter (E) produced by these in spleen and BM on days 5 and 21 after WT (black circles) or TLR7 KO (open circles) memory B cell transfer. (F,G) ELISPOT assays were used to determine the number (F) of Qβ specific PCs and the spot diameter (G) in the spleen and BM on day 5 after WT (black shapes) or TLR7 KO (open shapes) memory B cell transfer and challenge with Qβ-RNA, Qβ-PGA, or Qβ-CpG, respectively. Mean with SEM. P-values were obtained using an unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. n = 4 mice per group. Data representative of 2 (B–E) or 1 (F,G) independent experiments.