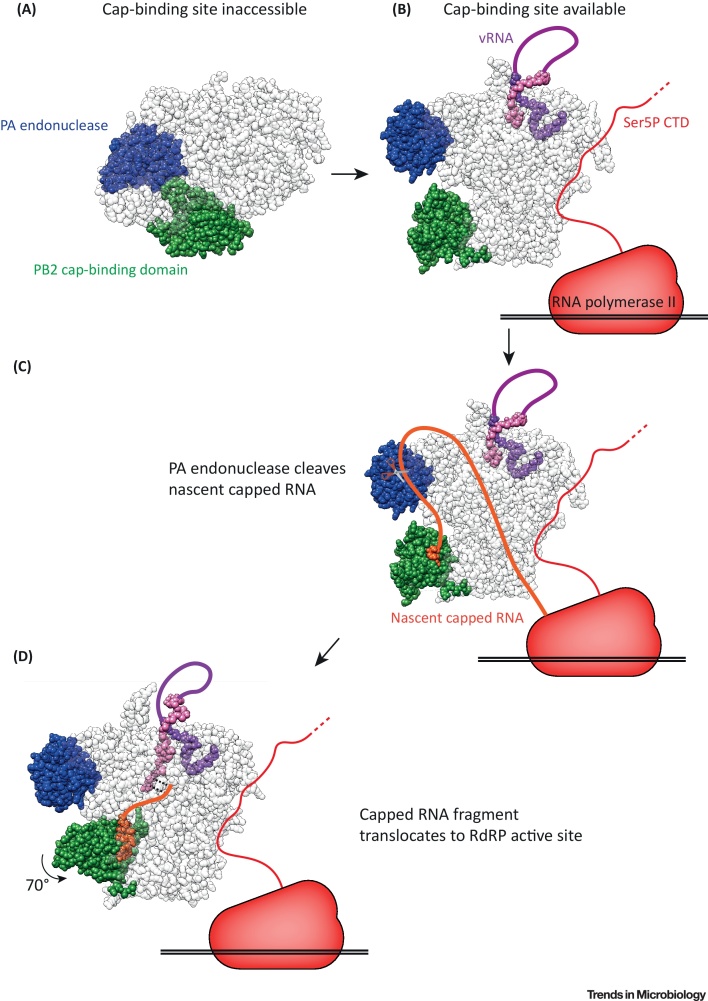
Figure 3.
Influenza RdRP Conformational Rearrangements during Cap Snatching. (A) In the transcriptionally inactive RdRP conformation, the PB2 cap-binding domain (green) is inaccessible and cannot bind capped RNA (PDB:5D98). (B) When influenza RdRP binds to vRNA and Ser5P Pol II CTD the transcriptionally active conformation is favoured. In this conformation the PB2 cap-binding domain is accessible, and is orientated towards the PA subunit endonuclease domain (blue) (PDB:4WSB). (C) Influenza RdRP binds to nascent capped RNA (orange), then the PA endonuclease cleaves 10–13 nt downstream of the m7G cap (PDB:6EVK). (D) Following cleavage, the PB2 cap-binding domain rotates by 70 degrees. This moves the capped RNA fragment away from the PA endonuclease and into the RdRP active site through the product exit channel. The capped RNA fragment can then base pair with the 3′ end of the vRNA template (pink) in the active site (PDB:5MSG).