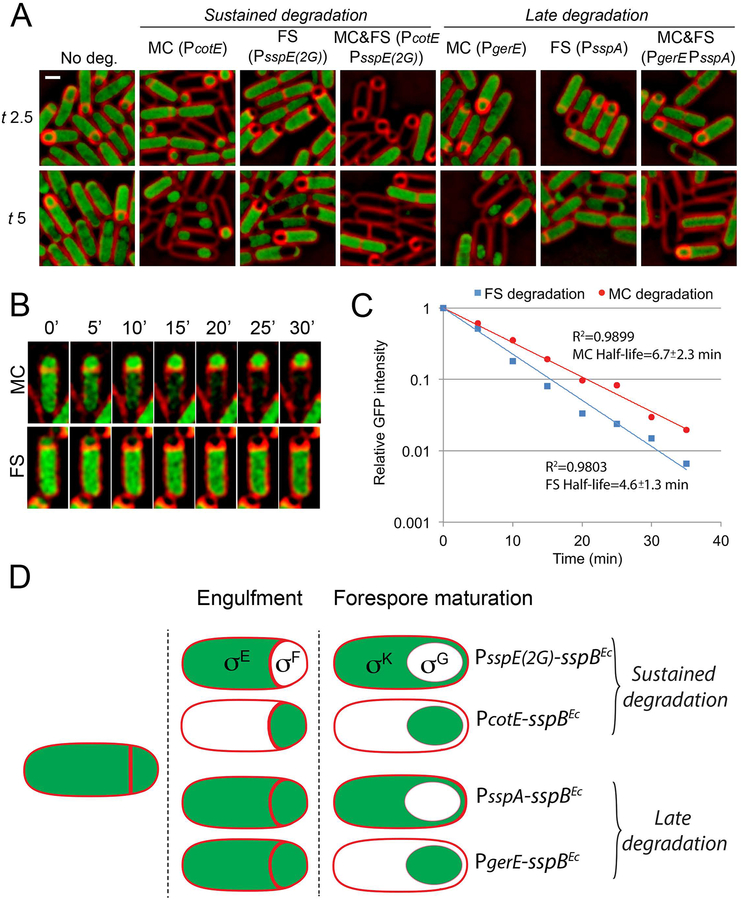
Figure 4. Cell- and stage-specific degradation of vegetative proteins.
A. Fluorescence microscopy showing the cell-specific degradation of YtsJ-GFP-ssrA*. SspBEc was produced from sustained promoters (indicated in parentheses) in the mother cell (MC), forespore (FS), or both (MC&FS) to induce the sustained degradation of YtsJ-GFP-ssrA*. To induce degradation only after engulfment (late degradation), sspBEc was expressed from late promoters. Membranes were stained with FM 4–64. Scale bar, 1 μm.
B. Timelapse microscopy showing the disappearance of YtsJ-GFP-ssrA* fluorescence signal when degradation is induced in the mother cell (MC, sspBEc expressed from PcotE) or in the forespore (FS, sspBEc expressed from PsspE(2G)). Images taken every 5 minutes are shown. Membranes were stained with FM 4–64.
C. YtsJ-GFP-ssrA* degradation kinetics when SspBEc is produced in the forespore (blue squares and line) or in the mother cell (red circles and line). In both cases, the disappearance of the GFP signal follows an exponential decay. The coefficient of determination of the regression curves (R2), and the half-lives of YtsJ-GFP-ssrA* when degradation is induced in the mother cell or the forespore are indicated in the graph. Data represent the average of 17 and 14 sporangia for forespore and mother cell degradation, respectively.
D. STRP setup. The use of sustained promoters (PsspE(2G) and PcotE) allows the sustained degradation of target proteins in the mother cell or the forespore. Expression of sspBEc from late promoters (PsspA and PgerE), however, triggers degradation of target proteins only after engulfment is completed. The combination of both classes of cell-specific promoters allows the evaluation of the spatial and temporal requirement of proteins made before polar septation.