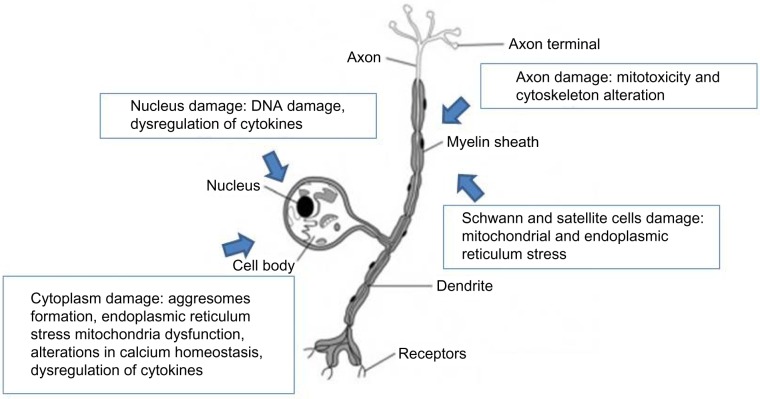
Figure 1.
Principal mechanisms of neuronal damage induced by bortezomib: ubiquitinated protein accumulated in the cytoplasm with production of aggresomes, endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondria dysfunction, axonal transport damage due to mitotoxicity and cytoskeleton alteration, DNA damage, and dysregulation of cytokines.