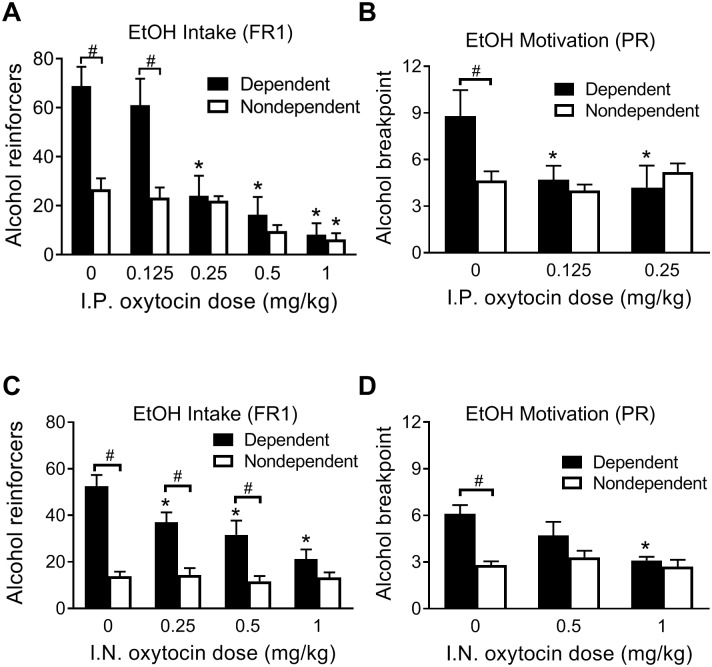
Fig 1. Effect of intraperitoneal and intranasal oxytocin on alcohol intake (FR1) and motivation (PR).
(A) Effect of intraperitoneal oxytocin on alcohol reinforcers earned by dependent and nondependent rats in 30-min alcohol self-administration sessions. (B) Effect of intraperitoneal oxytocin on breakpoint for alcohol on a PR schedule of reinforcement. (C) Effect of intranasal oxytocin on alcohol reinforcers earned by dependent and nondependent rats in 30-min alcohol self-administration sessions. (D) Effect of intranasal oxytocin on breakpoint for alcohol on a PR schedule of reinforcement. #Significant difference between dependent and nondependent rats (p < 0.05). *Significantly different from groups’ respective control condition (0 mg/kg; p < 0.05). EtOH, ethanol; FR1, fixed ratio 1; IN, intranasal; IP, intraperitoneal; PR, progressive ratio.