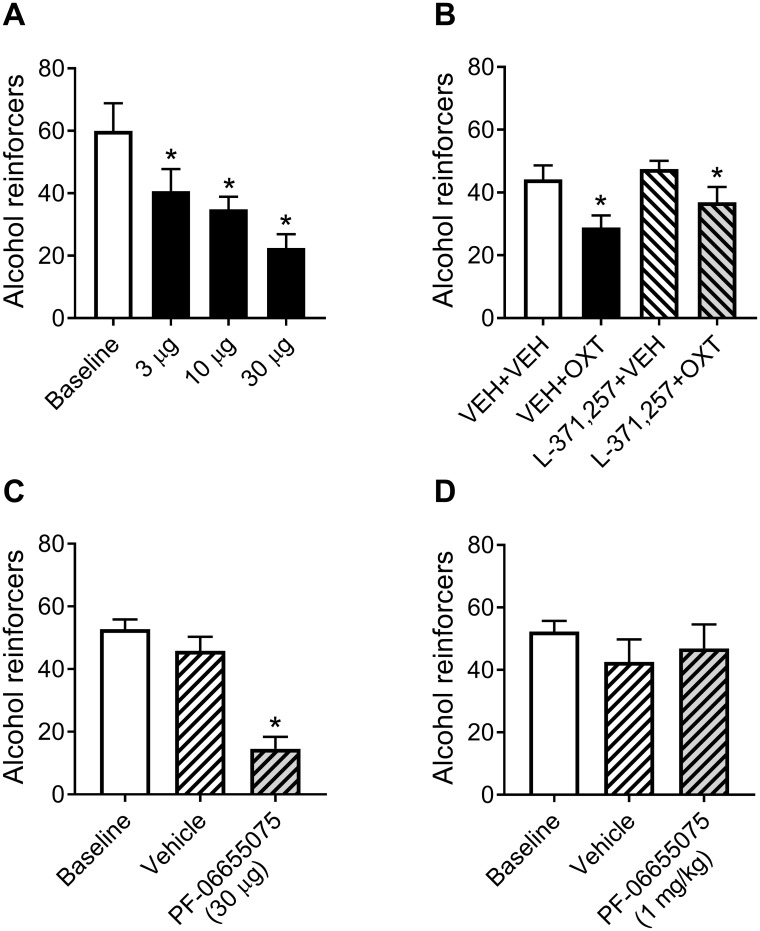
Fig 3. Central versus peripheral mediation of OXT’s effect on alcohol intake.
(A) Effect of intracerebroventricular infusion of OXT on alcohol reinforcers earned by dependent rats in 30-min alcohol self-administration sessions. (B) Effect of peripheral administration (intraperitoneal) of the OXT receptor antagonist L-371,257 that does not cross the blood-brain barrier on the ability of intranasal OXT to reduce alcohol reinforcers earned by dependent rats in 30-min alcohol self-administration sessions. (C) Effect of central (intracerebroventricular) administration of the OXT receptor agonist (PF-06655075, a long-acting, large molecule that does not cross the blood-brain barrier), on reinforcers earned by dependent rats in 30-min alcohol self-administration sessions. (D) Effect of systemic (subcutaneous) administration of PF-06655075 on reinforcers earned by dependent rats in 30-min alcohol self-administration sessions. *Significantly different from baseline or VEH condition (both in the case of panel C) (p < 0.05). OXT, oxytocin; VEH, vehicle.