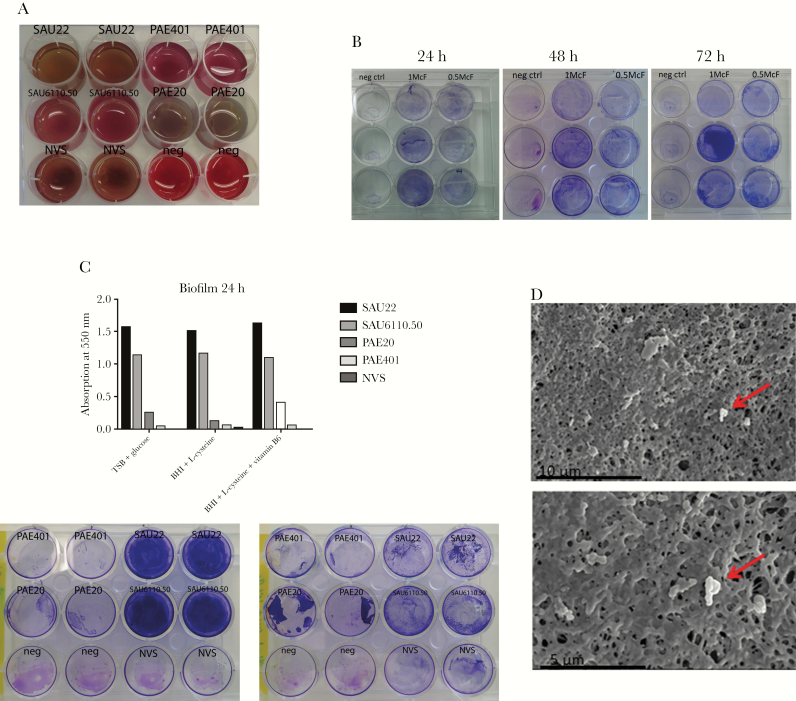
Figure 1.
A, Broth media incubating 2 Staphylococcus aureus strains (clinical isolate obtained from a patient with a proved cardiac implantable electronic device [CIED] infection [SAU6110.50] and a laboratory quality control strain [SAU22]) and 2 Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains (clinical isolate from a patient with cystic fibrosis [PA401] and a laboratory quality control strain [PAE20]). Aggregation of bacteria was macroscopically evident in broth incubating P. aeruginosa (strain PAE20). B, Crystal violet (CV) staining with inocula of 0.5 and 1.0 McFarland (McF) Granulicatella adiacens and incubation durations of 24, 48, and 72 hours. Overall, the dye uptake is poor. C, Differences between the CV staining of S. aureus or P. aeruginosa and G. adiacens in the results from absorption measurements (top) and wells (bottom). D, Scanning electron microscopic images of the polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bead biofilm formation assay show few adherent bacteria (red arrows) detected on the PMMA surface. Abbreviations: BHI, brain-heart infusion broth; neg ctrl, negative control; neg, negative control; NVS, nutritionally variant streptococci; TSB, tryptic soy broth.