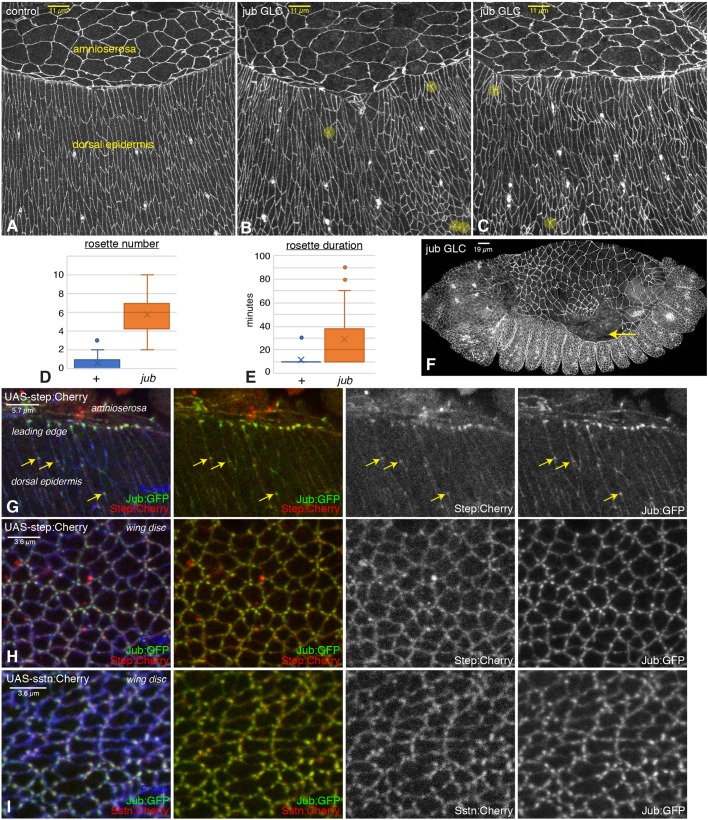
Fig. 4.
Embryonic phenotypes of jub and colocalization with Step. (A–C) Dorsal epidermal cells of wild-type (A) and jub germ line clone (B,C) embryos. Examples of rosettes are marked by yellow circles. (D,E) Quantification of average rosette number per half embryo at each time point (D) and duration of rosettes (E) from live embryos imaged every 10 min during the last 2 h of dorsal closure displayed as a Tukey box plot, with X marking the mean. (F) Example of jub embryo with detachment of amnioserosa from the leading edge (arrow). (G) Colocalization of Jub (green/white) with Step (red/white) in the dorsal epidermis and leading-edge cells of embryos expressing UAS-step:Cherry under da-Gal4 and act-Gal4 control. Arrows highlight examples of Jub and Step colocalization in the dorsal epidermis. (H) Colocalization of Jub (green) with Step (red) in wing disc cells expressing UAS-step:Cherry under nub-Gal4 control. (I) Colocalization of Jub (green) with Sstn (red) in wing disc cells expressing UAS-sstn:Cherry under nub-Gal4 control.