FIGURE 1.
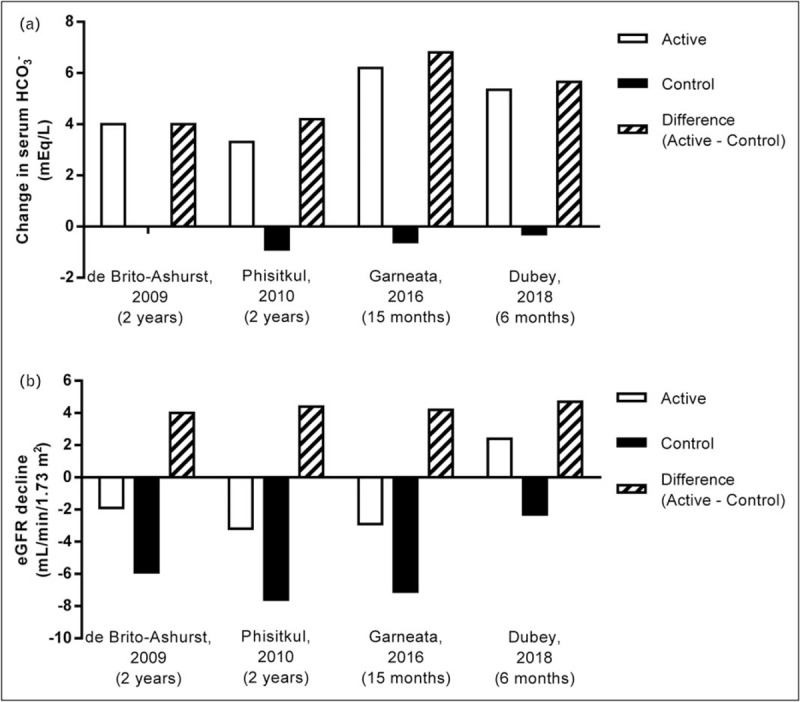
Serum bicarbonate (HCO3) increase and eGFR decline in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients with metabolic acidosis (serum HCO3 <22 mEq/l) treated with NaHCO3 or sodium citrate supplementation versus control. Summary of changes in serum HCO3 (panel a) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline (panel b) in CKD patients with metabolic acidosis (serum HCO3 <22 mEq/l) treated with NaHCO3 or sodium citrate supplementation (active) versus control patients. Data were extracted from the respective studies listed on the x-axis and cited in the reference section [15,16▪▪,17,18▪▪]; all values are mean changes from beginning to the end of the treatment period. The mean serum HCO3 values at the end of treatment for the de Brito-Ashurst et al. [15] study were estimated from graphed data. CKD, chronic kidney disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HCO3, bicarbonate.
