Figure 3.
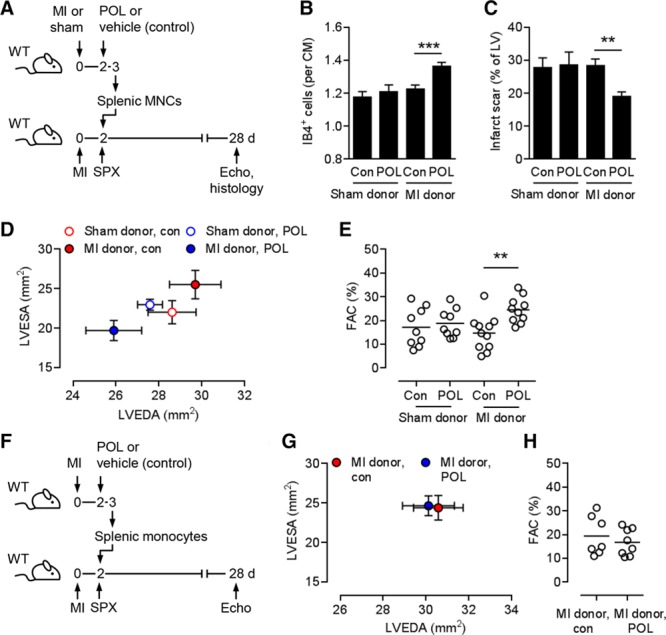
Importance of splenic MNCs for the therapeutic effects of POL5551. A, Experimental setup for B through E. Sham or myocardial infarction (MI) surgeries were performed in wild-type (WT) donor mice. Two days after MI, donor mice were intraperitoneally injected with POL5551 (POL) or vehicle only (control), and splenic mononuclear cells (MNCs) were isolated 24 hours later. Recipient WT mice underwent MI surgery, were splenectomized after 2 days, and then were infused intravenously with donor MNCs. Echo indicates echocardiography; and SPX, splenectomy. B through E, 9 to 11 mice per group. B, Fluorescein-labeled isolectin B4 (IB4)+ capillary density in the infarct border zone 28 days after MI. CM indicates cardiomyocyte; and Con, control. C, Scar size 28 days after MI. LV indicates left ventricle. D, LV end-diastolic area (LVEDA) and LV end-systolic area (LVESA) as determined by echocardiography 28 days after MI. LVESA: P<0.05, recipients receiving MNCs from infarcted POL5551-treated vs infarcted vehicle-only–treated donors (2-independent-sample t test). E, Fractional area change (FAC). F, Experimental setup for G and H. MI was induced in WT donor and recipient mice. Two days after MI, donor mice were intraperitoneally injected with POL5551 or vehicle only (con), and splenic monocytes were isolated 24 hours later. Two days after MI, recipient mice were splenectomized and then infused intravenously with donor monocytes. Seven to 8 mice per group. G, LVEDA and LVESA 28 days after MI. H, FAC. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (2-independent-sample t tests).
