Figure 4.
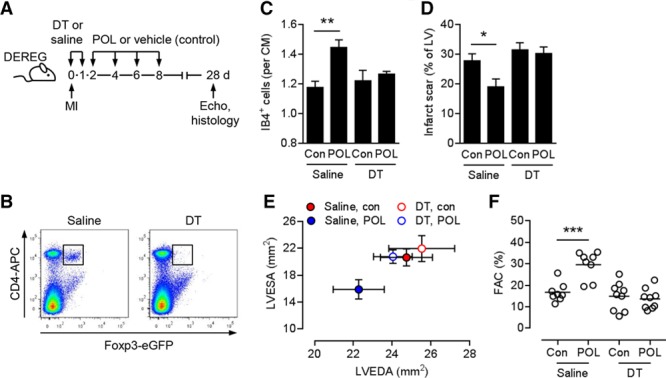
Importance of regulatory T cells for the therapeutic effects of POL5551. A, Experimental setup. Myocardial infarction (MI) was induced in DEREG mice. Diphtheria toxin (DT) or saline was intraperitoneally injected immediately before and 24 hours after MI. POL5551 (POL) or vehicle only (control) was intraperitoneally injected 2, 4, 6, and 8 days after MI. Echo indicates echocardiography. B, Representative flow cytometry panels confirming CD4+ Foxp3+/eGFP+ regulatory T cell depletion in splenocytes 24 hours after the second DT injection. C through F, Eight to 9 mice per group. C, Fluorescein-labeled isolectin B4 (IB4)+ capillary density in the infarct border zone 28 days after MI. CM indicates cardiomyocyte; and Con, control. D, Scar size 28 days after MI. LV indicates left ventricle. E, LV end-diastolic area (LVEDA) and LV end-systolic area (LVESA) as determined by echocardiography 28 days after MI. LVESA: P<0.05, POL5551 vs control in saline-injected mice (2-independent-sample t test). F, Fractional area change (FAC). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (2-independent-sample t tests).
